What Are Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films? Benefits, Applications, and Production
Fast dissolving oral thin films (OTFs) are innovative drug delivery systems designed to rapidly disintegrate and dissolve in the oral cavity without the need for water. These ultra-thin films, typically made from polymeric materials, incorporate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and are designed to provide convenience, improved bioavailability, and enhanced patient compliance, especially for populations with swallowing difficulties such as children and the elderly.
OTFs are becoming increasingly popular owing to their quick onset of action, ease of administration, and portability. They are particularly suitable for drugs that require rapid relief, have poor water solubility, or benefit from bypassing first-pass metabolism.
How Do Oral Thin Film Drugs Work?
OTFs drugs function by rapidly disintegrating upon contact with saliva within the oral cavity. When placed on the tongue or any other mucosal surface, the film quickly dissolves or disintegrates, releasing the drug. The API is then absorbed through the rich blood supply in the oral mucosa or swallowed with saliva for absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Key steps in their mechanism include:
Rapid disintegration: The film's formulation enables it to break down within seconds to a few minutes.
Absorption: The drug can be absorbed directly through the mucous membranes (for fast onset) or swallowed for absorption through the gastrointestinal system.
Bioavailability: By bypassing hepatic first-pass metabolism, some drugs exhibit improved bioavailability when delivered via OTFs.
What is an Oral Thin Film?
Why Are Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films Needed?
Fast dissolving oral thin films are highly beneficial for several reasons. They significantly enhance patient compliance by being easy to administer, which is especially advantageous for children, the elderly, or patients with swallowing disorders (dysphagia). Their rapid disintegration ensures quick absorption of the drug, leading to faster therapeutic effects. Additionally, these films offer unmatched convenience and portability; they are thin, lightweight, and discreet, allowing patients to take them anytime and anywhere without the need for water. Moreover, they often provide improved stability for sensitive drugs by avoiding aqueous formulations that could degrade the active ingredients. Finally, oral thin films are versatile in design, making it possible to customize doses and even incorporate multiple drugs into a single film, further increasing their appeal and efficacy as a drug delivery system.
Advantages of Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films
Rapid onset of action due to quick disintegration and absorption in the oral cavity
No need for water, making them ideal for on-the-go use
Improved patient compliance, especially for children, elderly, or those with dysphagia
Bypasses first-pass metabolism in some cases, enhancing bioavailability
Easy to carry and store due to compact, lightweight design
Customizable dosing, including multi-drug combinations in one film
Improved stability for moisture-sensitive APIs
Masking of unpleasant taste through flavoring agents and coating layers
Suitable for continuous manufacturing using scalable techniques like slot-die coating
Disadvantages of Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films
Limited drug loading capacity, especially for high-dose medications
Moisture sensitivity may require special packaging to prevent degradation
Mechanical fragility—films can be delicate and prone to tearing
Complex formulation requirements to balance disintegration, taste, and stability
Higher production costs compared to conventional oral dosage forms
Limited compatibility with all types of APIs (e.g., highly hydrophobic drugs)
Regulatory challenges in standardizing new delivery formats across markets
Discover how lab-scale slot-die coating improves pharmaceutical and medical device development through precise, uniform coatings for testing and prototyping.
The Importance of Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films
An oral thin film drug delivery system typically consists of multiple functional layers, each serving a specific purpose to ensure the film's performance, stability, and palatability. The base or substrate layer provides the structural support and flexibility for the film and is usually made from materials such as PET, polyethylene, or cellophane.
Directly above this is the polymer or matrix layer, which contains the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) embedded within hydrophilic polymers like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), or pullulan; this layer facilitates rapid disintegration and drug release. In many formulations, the drug itself is dispersed within this matrix, although in some multi-layer designs, the drug may reside in a dedicated layer for controlled release.
To enhance patient acceptability, flavoring and sweetening agents—such as fruit flavors and sweeteners like sorbitol—are incorporated either directly into the main film or as separate layers. Optional layers include a release or coating layer designed to modulate the release profile or mask taste, made from film-forming or enteric polymers, and a protective or sealant layer that provides a barrier against moisture, oxygen, or contamination, especially during storage.These protective layers often utilize foil, laminate, or moisture-impermeable materials to maintain stability. The combination of these layers creates a versatile and effective drug delivery platform that is customizable to meet specific therapeutic and patient needs.
| Layer Type | Function | Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate / Support | Structural support, flexibility | PET, PE, cellulose |
| Polymer / Matrix Layer | Embeds drug, supports disintegration | HPMC, PVA, pullulan |
| Drug Layer | Contains active pharmaceutical ingredient | The API in dispersed form |
| Flavor/Sweetener Layer | Masks taste, improves acceptability | Sucrose, sorbitol, flavor oils |
| Release/Coating Layer | Controls drug release, taste masking | Enteric coatings, film-forming polymers |
| Protective Sealant Layer | Enhances stability, moisture barrier | Foil, laminate, moisture barriers |
Application of Slot Die Coating in Research and Development of Oral Thin Films
Slot-die coating is a precision coating technique widely used in the manufacturing of OTFs during research and development (R&D), as well as at the production scale. It offers excellent control over film thickness, uniformity, and coating quality—critical factors for drug efficacy and safety.
How slot die coating is utilized:
Film Formation: In R&D, researchers use slot die coating to deposit uniform layers of polymer-drug solutions onto flexible substrates (like PET or other films). The process allows precise adjustment of parameters such as coating speed, gap size, and solution flow rate to optimize film thickness and uniformity.
Formulation Screening: Researchers can rapidly prototype different formulations by adjusting the coating parameters, enabling efficient comparisons of drug load, dissolution rate, and mechanical properties.
Scale-Up and Production: Slot-die coating's ability to produce high-quality, consistent films makes it suitable for scaling up from laboratory to pilot and commercial manufacturing.
Optimization of Parameters: The technique permits detailed control over variables such as viscosity, drying conditions, and coating speed, facilitating the development of robust, reproducible films suitable for clinical and commercial use.
Advantages of slot die coating in OTF development include:
High precision and uniformity
Compatibility with continuous manufacturing
Minimal waste of materials
Ability to coat complex formulations with sensitive active ingredients
Learn the complete process of creating uniform thin films using a slot-die coater.
Conclusion
Fast dissolving oral thin films are transforming drug delivery by offering rapid onset, ease of use, and improved patient compliance. Their versatility, especially for populations with swallowing difficulties, makes them an attractive option for a wide range of therapeutic areas. When combined with precision techniques like slot-die coating, these films can be developed with excellent uniformity, consistency, and scalability. This makes it easier to transition from laboratory research to full-scale production, supporting the development of safer, more effective, and patient-friendly pharmaceutical products.
Get Professional Support for Your Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.
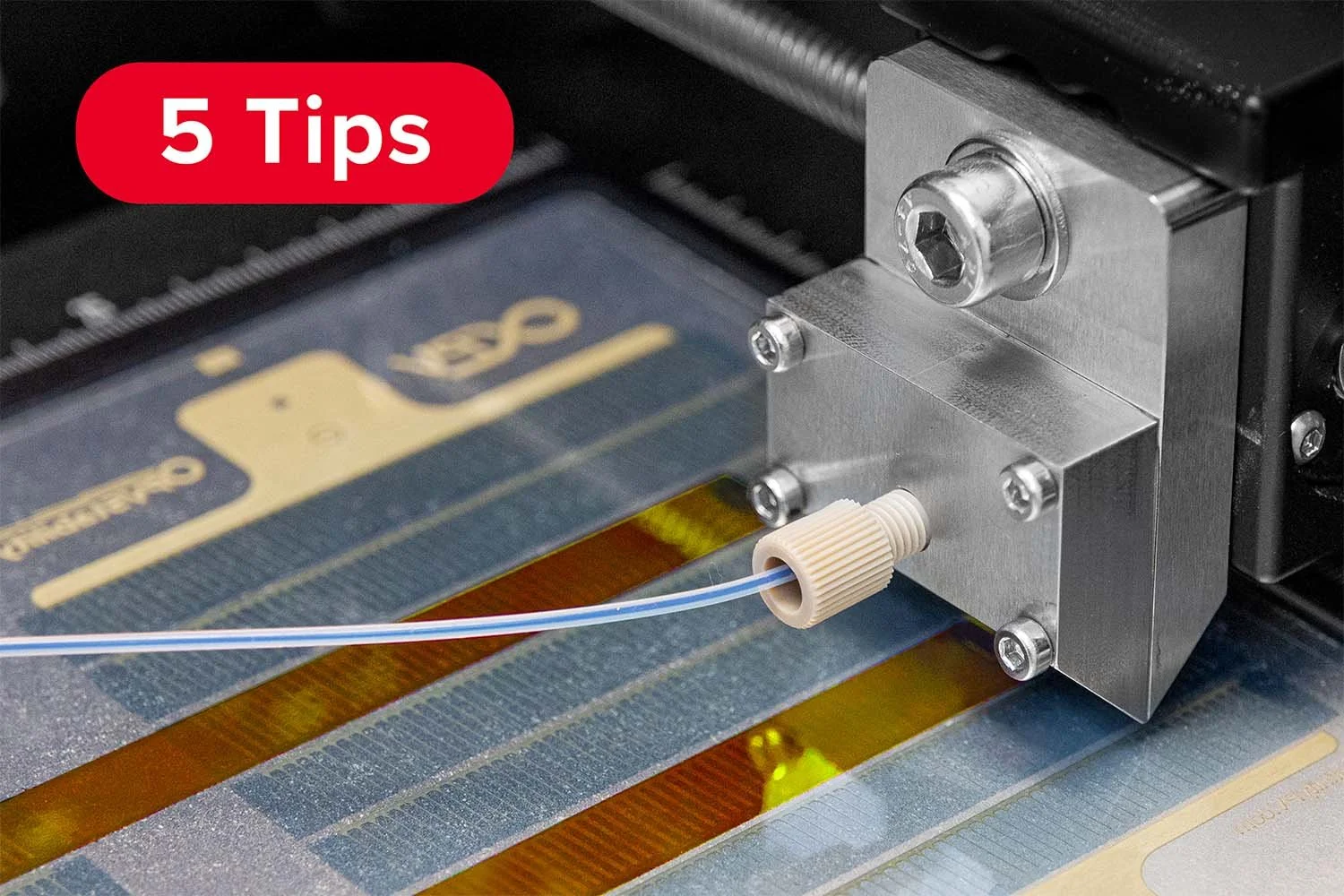
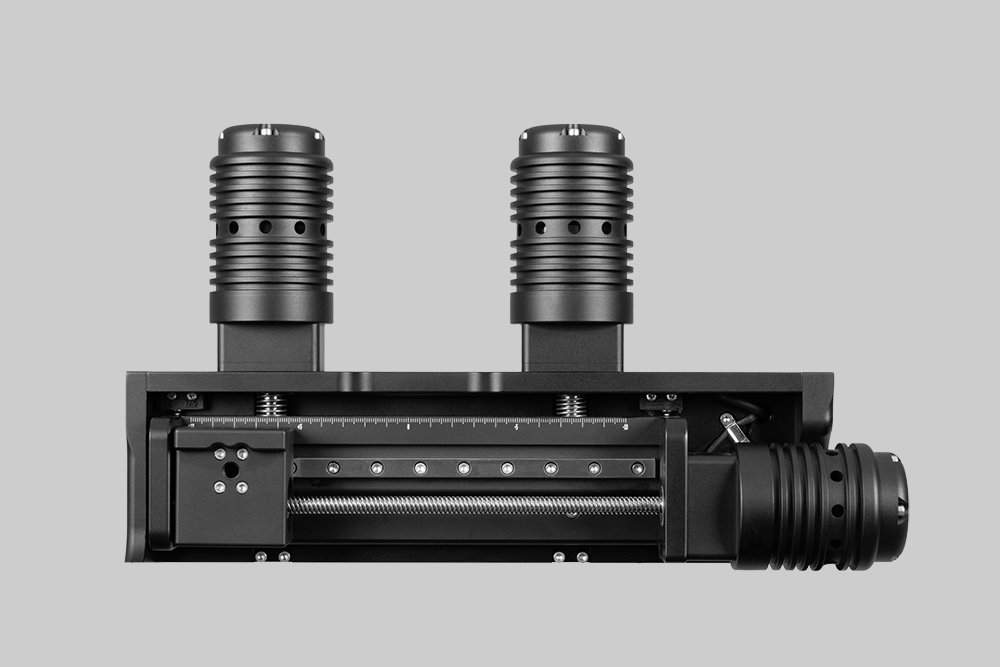




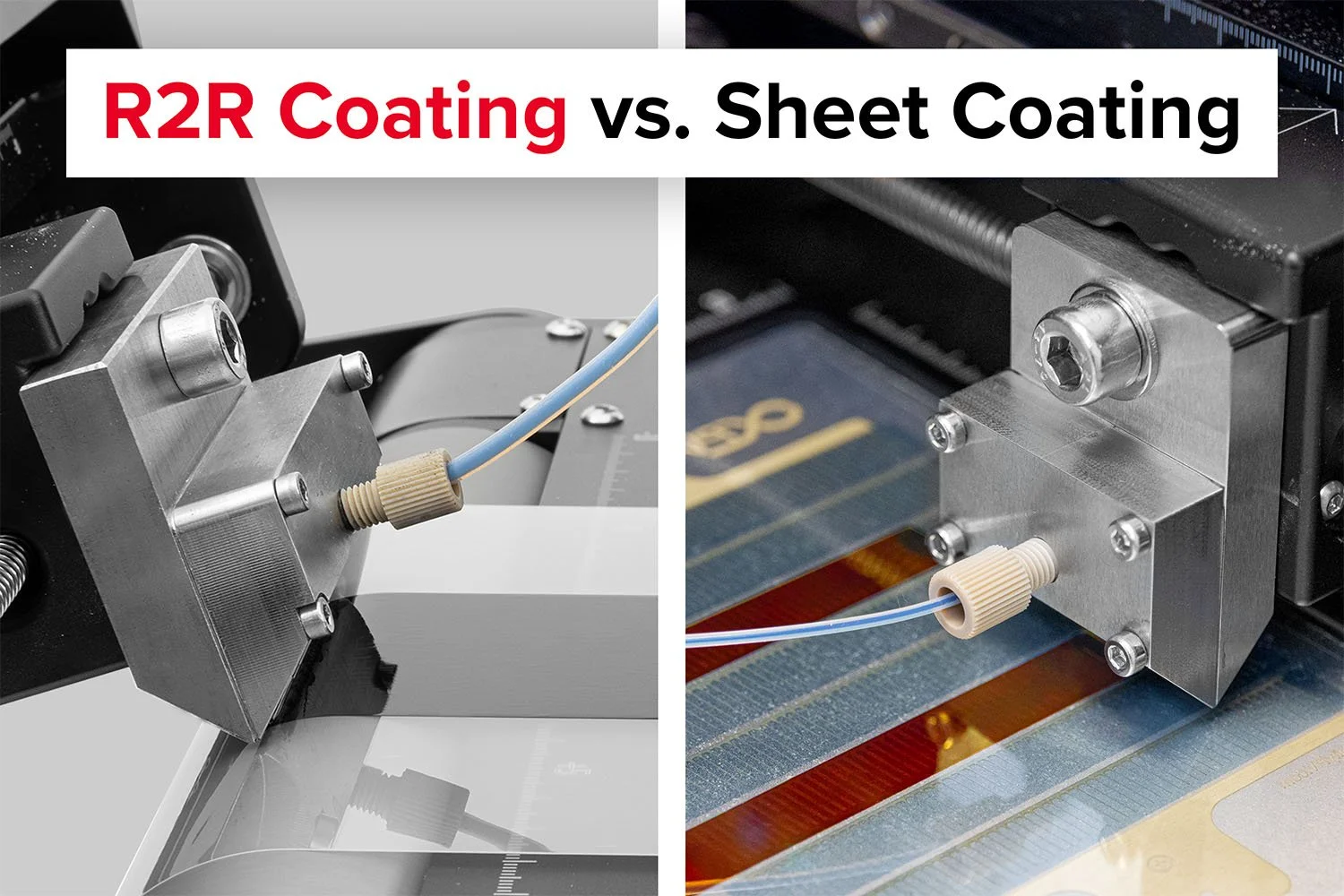




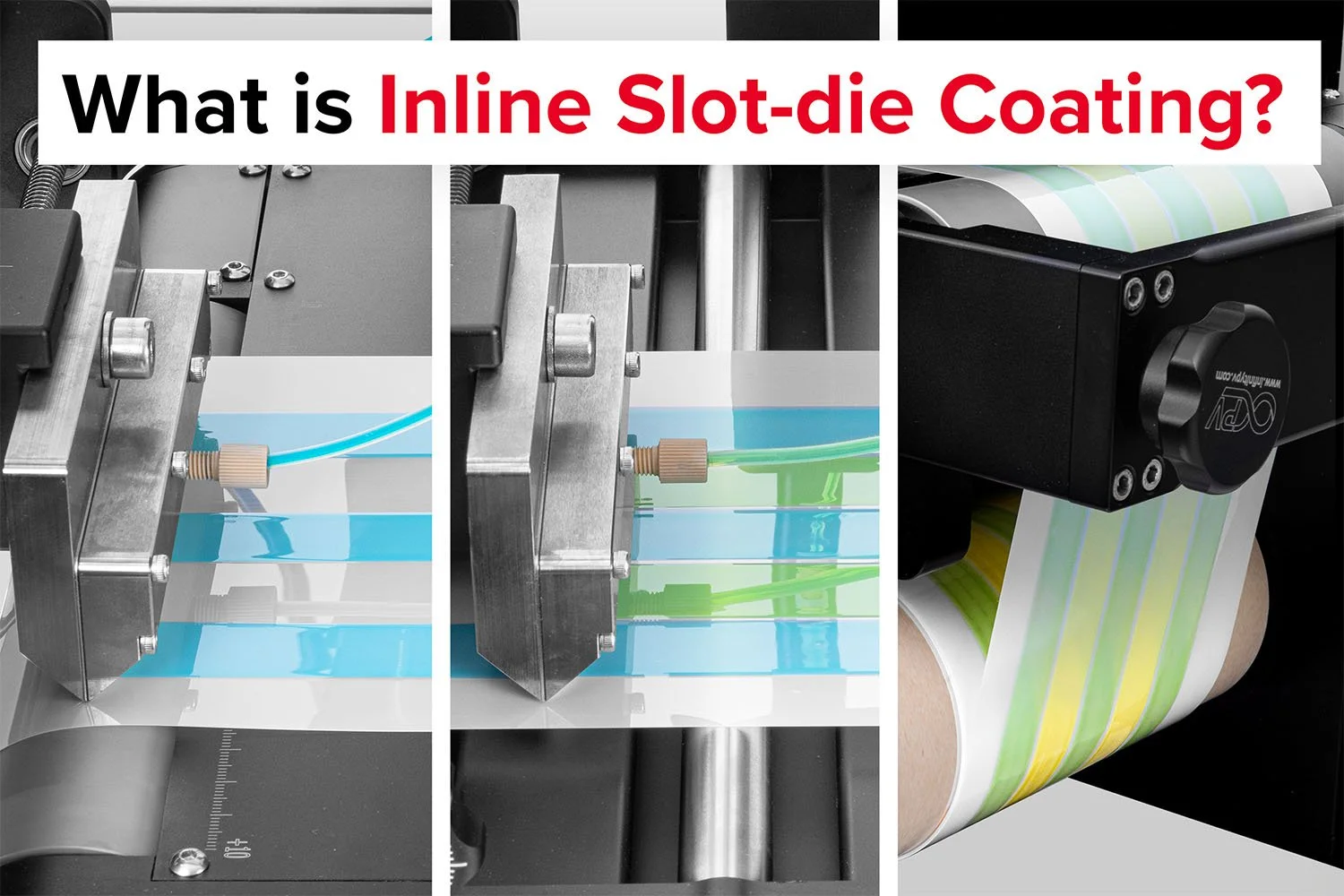














Probably the World’s Most Compact R2R Slot-die Coater: A compact, fully integrated roll-to-roll coating platform for laboratories, complete with a mounting system, anodized rollers, a syringe pump, a 65 mm stainless slot-die head and an infrared oven system—delivering unmatched precision and scalability.