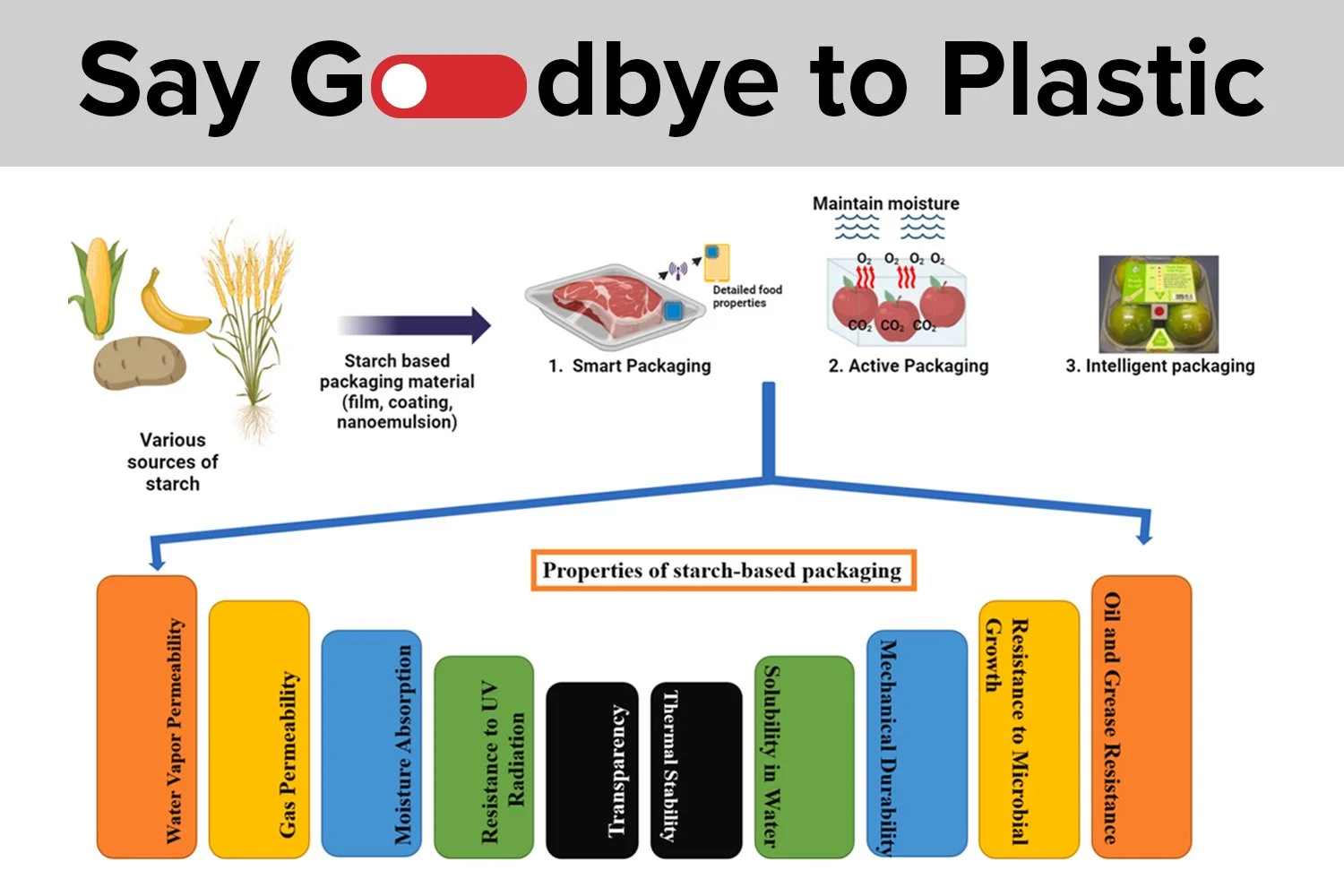
Sustainable Food Packaging: Slot-die Coating and Starch-Based Films
In an era defined by environmental consciousness and the pressing need for sustainable alternatives, the packaging industry has been under immense pressure to innovate. Traditional petroleum-based plastics, while ubiquitous, contribute significantly to global pollution, necessitating a shift towards biodegradable and renewable materials.
Enter starch-based films. A promising solution derived from natural sources that offer a viable alternative for food packaging.
The Promise of Starch-Based Films
Starch, an abundant polysaccharide found in corn, potatoes, and cassava, has emerged as a frontrunner in the quest for sustainable packaging materials. Its renewability, low cost, and inherent biodegradability make it an attractive substitute for conventional plastics. Starch-based films are not only safe for food contact but also offer the potential to be used in edible coatings and pharmaceutical capsules.
Overcoming Limitations through Innovation
Despite their advantages, native starch films face challenges such as poor mechanical strength, water sensitivity, and limited barrier properties. To address these shortcomings, researchers have explored various innovative approaches:
Polymer Modifications: Altering the structure of starch through chemical, physical, and enzymatic methods to enhance its thermal stability, mechanical strength, and water resistance.
Nanocomposite Incorporation: Reinforcing starch matrices with nano-sized materials like cellulose nanocrystals, montmorillonite clay, or graphene oxide to improve barrier properties and mechanical performance.
Active and Intelligent Packaging: Integrating bioactive compounds such as antioxidants and antimicrobial agents, as well as smart indicators that respond to changes in food quality, to extend shelf life and enhance consumer safety.
Blending with Hydrophobic Polymers: Combining starch with polymers such as poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (caprolactone) (PCL), improving the material and increasing water resistance and decreasing water solubility.
Innovative Processing Techniques: Cold plasma which induces alterations in the polymeric matrix, enhancing and refining the attributes of starch granules, improving their performance as a packaging material.
Cross-linking Method: Cross linking starch molecules through physical and chemical methods demonstrated potential in reducing it's water solubility while maintaining it's mechanical integrity.
Esterifying Starch: Esterifying starch with organic acids introduces hydrophobic groups which translates into lower water absorption and improved thermoplasticity.
Slot-Die Coating: A Versatile Technique for R&D
Slot-die coating is a versatile and precise method for depositing thin films onto various substrates, making it invaluable for the research and development of starch-based films. This technique offers several advantages, including uniformity, as it ensures consistent film thickness, which is critical for reproducible performance in packaging applications.
Additionally, controllability is a key feature, as the coating thickness, speed, and flow rate can be precisely controlled, allowing for systematic optimization of film properties.
Scalability is another benefit, as slot-die coating can be scaled up for continuous production, making it suitable for both laboratory research and industrial applications. Furthermore, this method is versatile and can accommodate a wide range of formulations, including starch blends, nanocomposites, and active packaging materials.
Applications of Slot-Die Coating in Starch Film R&D
Optimizing Film Composition: Slot-die coating can be used to deposit films with varying ratios of starch, plasticizers, and additives, enabling researchers to identify the ideal composition for desired mechanical and barrier properties.
Developing Multilayer Films: This technique allows for the creation of multilayer films with different functionalities, such as a starch-based layer for biodegradability and a hydrophobic coating for moisture resistance.
Incorporating Active Agents: Slot-die coating can be employed to apply thin layers of antimicrobial or antioxidant agents onto starch films, providing controlled release and enhancing food preservation.
Creating Smart Packaging: By coating starch films with pH-sensitive or gas-responsive indicators, slot-die coating facilitates the development of intelligent packaging that monitors food freshness and spoilage.
What is roll-to-roll processing, and why is it revolutionizing the way we make flexible devices?
Lamination: A Powerful Strategy for Enhanced Functionality
Lamination, the process of bonding multiple layers of materials together, has emerged as a powerful strategy in both the production and the research and development of starch-based food packaging films. This technique allows for the strategic combination of different material properties, overcoming the inherent limitations of starch films and creating packaging solutions with tailored functionality.
How Lamination is Used
Combining Properties: Lamination allows researchers and manufacturers to combine the strengths of different materials. For instance, you might laminate a starch-based layer (for biodegradability and low cost) with a thin layer of a different biopolymer or even a very thin petroleum-based polymer (for improved moisture barrier, oxygen barrier, or mechanical strength).
Discover how pristine clean surface coating eliminates defects by applying functional layers onto untouched substrates. Ideal for medtech, solar cells, OLEDs, and advanced electronics.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
Despite significant progress, several challenges remain in scaling up starch-based film technologies for industrial production. These include:
Economic Viability: Balancing the cost of starch modifications and additives to ensure competitive pricing compared to conventional plastics.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent food contact regulations and migration limits for additives used in starch films.
Performance Consistency: Ensuring reproducible film properties across different starch sources and processing conditions.
Environmental Sustainability: Enhancing the biodegradability of starch films in various disposal environments, including composting and soil.
Conclusion
Starch-based films offer a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to conventional plastics, combining renewability, low cost, and safety for food contact. While native starch films have limitations in mechanical strength, water resistance, and barrier properties, innovations such as polymer modifications, nanocomposites, cross-linking, esterification, and blending with hydrophobic polymers have improved their performance. Advanced techniques like slot-die coating and lamination enable precise film formation, multilayer designs, and incorporation of active or intelligent packaging functions.
Challenges remain in scaling up production, including cost, regulatory compliance, consistency, and environmental performance. Continued research and innovation can help starch-based films meet these challenges, offering a path toward functional, safe, and environmentally responsible food packaging.
Get Professional Support for Your Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.
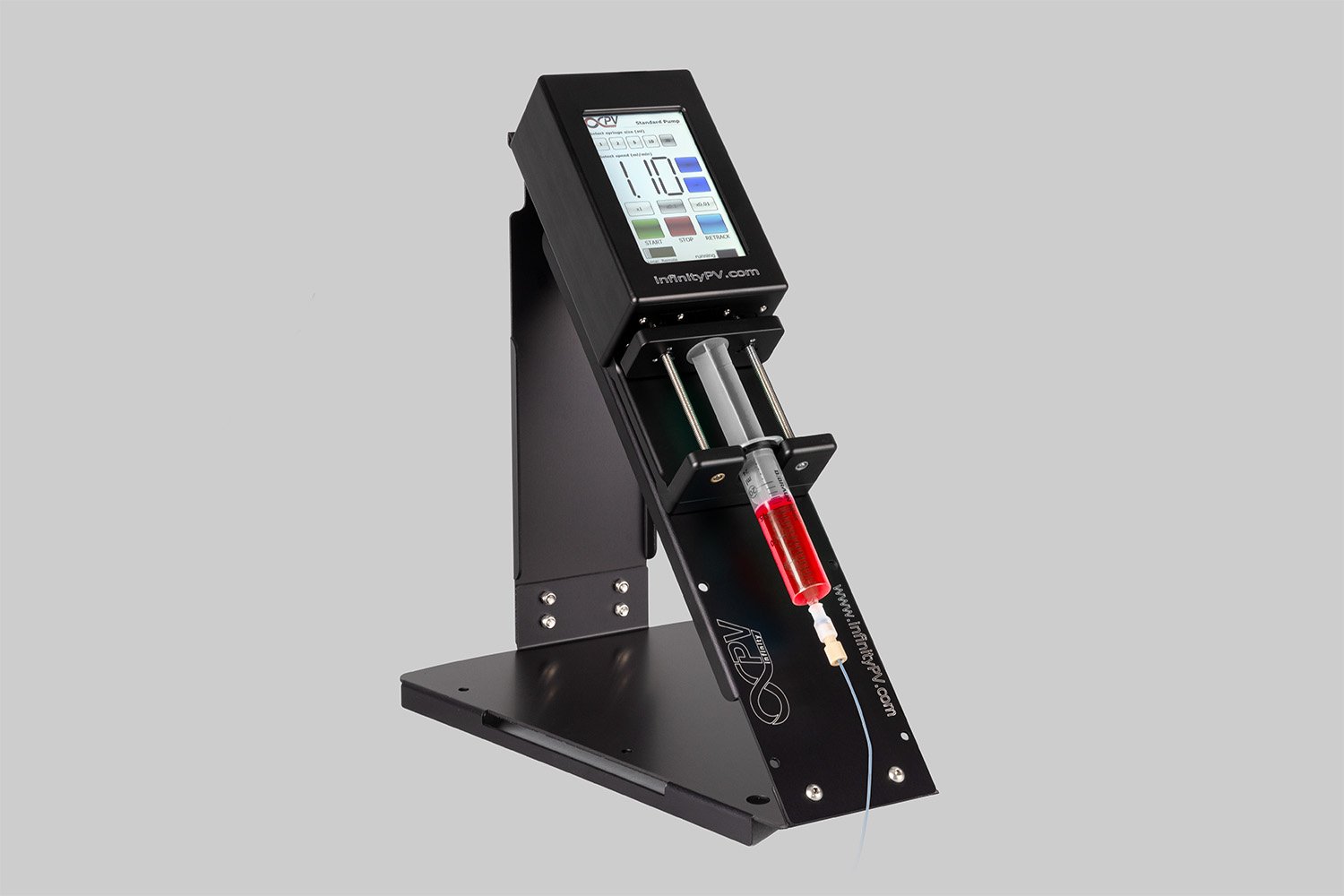















Probably the World’s Most Compact R2R Slot-die Coater: A compact, fully integrated roll-to-roll coating platform for laboratories, complete with a mounting system, anodized rollers, a syringe pump, a 65 mm stainless slot-die head and an infrared oven system—delivering unmatched precision and scalability.