What Are Drug Films and Nanocarriers? The Latest Research Into Modern Drug Delivery
Can Drugs Work Better Without Pills or Injections?
A recent review titled "Transmucosal Drug Delivery: Prospects, Challenges, Advances, and Future Directions" explores a timely and increasingly important question in pharmaceutical science: Can therapeutic drugs be delivered more effectively without relying on traditional pills or injections?
This review delves into the growing field of transmucosal drug delivery (TDD), which involves administering drugs through mucous membranes such as those found in the mouth, nose, eyes, and vagina. These routes present promising alternatives to conventional methods by offering faster absorption, fewer side effects, and improved patient comfort.
Traditional drug delivery systems face notable limitations. Oral drugs often degrade in the digestive tract or are diminished by first-pass liver metabolism before reaching the bloodstream, reducing their effectiveness. Injectable drugs, while effective, come with drawbacks such as pain, the need for trained healthcare personnel, and refrigeration requirements. These limitations have spurred interest in alternate drug delivery routes, particularly those that utilize the body's mucosal surfaces. The review provides a comprehensive assessment of these emerging methods and outlines how they are transforming modern pharmacotherapy.
Key Highlights
Transmucosal drug delivery avoids liver metabolism and gastrointestinal degradation, improving bioavailability.
Common mucosal sites include the oral (buccal and sublingual), nasal, ocular, rectal, and vaginal membranes.
These systems are minimally invasive and can significantly enhance patient compliance compared to traditional injections.
Advanced delivery systems such as mucoadhesive films, nanocarriers, and microneedles are being developed to improve retention and drug absorption.
Nose-to-brain delivery stands out for its ability to bypass the blood-brain barrier, offering potential in treating neurological diseases.
Challenges persist due to rapid clearance mechanisms, variations in mucosal tissue, and external factors like saliva or blinking.
Solutions include permeation enhancers, enzyme inhibitors, and pH stabilizers customized for specific mucosal surfaces.
Future developments will support targeted, on-demand dosing and align with the goals of personalized medicine.
Understanding the Technology: What is Transmucosal Drug Delivery?
Transmucosal drug delivery refers to the administration of therapeutic agents across mucous membranes instead of the more traditional oral or injectable routes. These membranes are found in various parts of the human body, including the mouth, nose, eyes, rectum, and vagina. Each of these tissues is highly vascularized, meaning they contain a rich supply of blood vessels, and they possess thin epithelial layers, which facilitate the absorption of drugs directly into the bloodstream.
The advantage of bypassing the digestive system and liver is significant. Drugs that are sensitive to enzymatic degradation in the gastrointestinal tract or that undergo extensive metabolism in the liver benefit immensely from this alternative route. Moreover, the non-invasive nature of TDD methods contributes to better patient compliance, especially among populations like children and the elderly who may struggle with swallowing pills or managing injectable therapies.
Beyond systemic delivery, TDD also allows for localized treatment. For instance, vaginal delivery systems can provide targeted therapy for reproductive health conditions, while ocular systems address eye-related diseases directly. The ability to provide both local and systemic effects makes transmucosal delivery a versatile and powerful approach in drug administration.
Why This Review Matters: The Significance of the Work
This review holds substantial value for both researchers and clinicians as it collates a decade's worth of advancements in TDD across multiple mucosal routes. Its strength lies in offering a comparative perspective on each site of delivery, highlighting their physiological advantages, specific limitations, and suitable drug types. The review is not only an academic contribution but also serves as a practical guide for pharmaceutical development.
The authors point out that the rise of biologics such as proteins, peptides, and RNA therapies necessitates new methods of delivery. These complex molecules do not fare well when taken orally due to their size and sensitivity. Transmucosal routes provide a feasible solution by allowing these large molecules to enter systemic circulation more directly and with greater efficiency.
In addition, the review emphasizes the clinical potential of TDD, particularly for populations with unique needs such as pediatric or geriatric patients. It also underscores the relevance of TDD in personalized medicine, where treatments can be tailored not only by drug type but also by delivery route and formulation design.
Learn the complete process of creating uniform thin films using a slot-die coater.
How the Review Was Conducted: Methods and Scope
The authors of this review gathered data from a range of reliable scientific databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, covering literature published between 2012 and 2025. They also consulted regulatory sources such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). By combining peer-reviewed articles with regulatory documentation, the review provides a balanced view of both scientific innovation and real-world application.
The study categorizes mucosal drug delivery systems based on the anatomical site and evaluates the efficacy of various formulations. The technologies examined include mucoadhesive films and wafers, nanoparticles, in-situ gels, and microneedles. Each method is analyzed for its ability to improve drug retention, bioavailability, and patient compliance.
Exploring the Nasal Route: A Gateway to the Brain
Among the mucosal delivery methods, nasal administration stands out due to its unique anatomical and physiological features. The nasal cavity offers a direct path to the systemic circulation, allowing drugs to bypass the liver. More importantly, it provides a rare opportunity to access the brain directly through the olfactory and trigeminal nerves. This capability makes it a promising route for treating neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
The review discusses how nasal formulations can be optimized to enhance their performance. Strategies include the use of mucoadhesive gels that prolong the formulation's contact with the mucosa, and nanocarriers that improve the drug's ability to penetrate biological barriers. Additionally, permeation enhancers and enzyme inhibitors can be included to facilitate the absorption of larger molecules.
Despite its promise, nasal delivery is not without challenges. The limited volume that can be administered intranasally, the presence of mucus, and the variability in individual nasal anatomy all contribute to inconsistent drug absorption. The review notes that novel delivery devices and improved formulation technologies are actively addressing these issues.
Achieve pristine, contamination-free coatings with the Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater.
Innovation in Formulations: The Role of Nanotechnology and Mucoadhesion
Advanced drug delivery systems are at the heart of TDD's success. The review highlights several innovative approaches that have significantly enhanced drug bioavailability and therapeutic outcomes. One such advancement is the development of mucoadhesive formulations. These formulations contain ingredients that allow them to stick to mucosal surfaces, thereby extending their residence time and increasing drug absorption.
Nanotechnology plays an equally crucial role. Nanoparticles can encapsulate drugs, protecting them from degradation and controlling their release. These particles can be engineered to penetrate mucus layers and cellular barriers, improving the delivery of challenging drugs like proteins and nucleic acids.
The combination of these two technologies, such as embedding nanoparticles within mucoadhesive films or wafers, has proven to be highly effective. This synergy allows for sustained release, targeted delivery, and improved patient outcomes across various therapeutic areas.
Looking Ahead: Future Outlook for TDD in the Industry
The future of transmucosal drug delivery appears promising and aligns closely with the trajectory of personalized medicine. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to embrace biologics and precision therapies, the demand for efficient, patient-friendly delivery systems will grow. TDD methods offer an ideal solution by allowing for localized or systemic treatment through convenient, non-invasive routes.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing and bio-responsive materials will further revolutionize this field. These tools can produce custom formulations that respond to specific physiological cues such as pH or temperature, enhancing drug release profiles. Regulatory support and collaborative efforts between academia and industry will be essential to overcome existing challenges and ensure these innovations reach the market.
Moreover, as global health systems seek cost-effective and accessible solutions, especially in low-resource settings, TDD presents a viable strategy. Formulations that do not require refrigeration and can be self-administered are particularly valuable in these contexts.
Choose the right slot-die head for your application Read our guide to understand which slot-die head is right for you.
Conclusion
Transmucosal drug delivery represents a significant evolution in the field of therapeutics. By offering an alternative to pills and injections, it opens up new possibilities for treating a wide range of conditions more effectively and comfortably. The review by Brako and Boateng provides a comprehensive guide to the current landscape and future potential of TDD, highlighting its advantages, challenges, and technological advancements.
As drug development continues to shift towards complex molecules and personalized approaches, TDD systems will become increasingly vital. This review serves as both a foundation and a catalyst for future innovation, signaling a new era in drug delivery science.
Authors
Francis Brako
Joshua Boateng
Get Professional Support for Your Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.
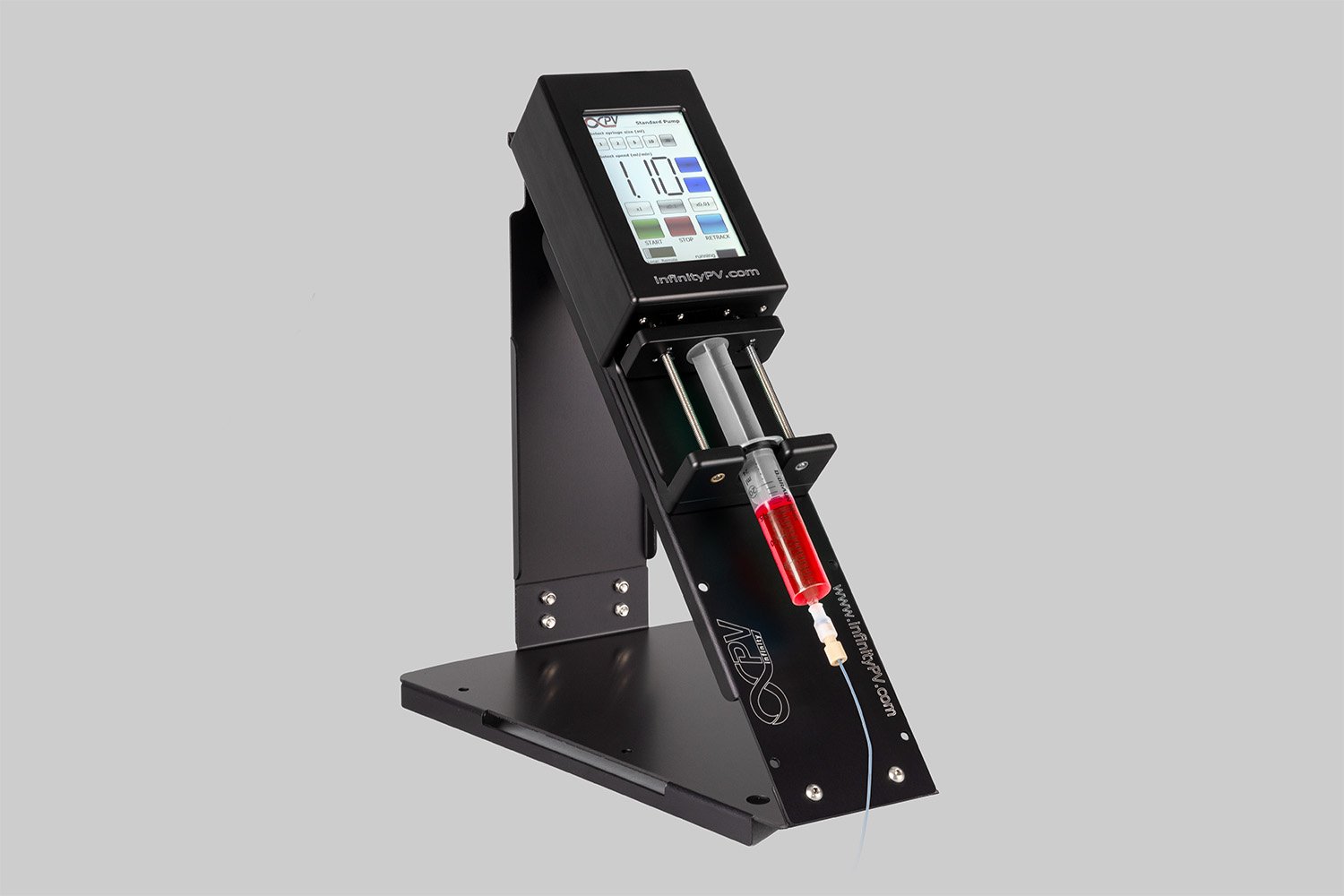
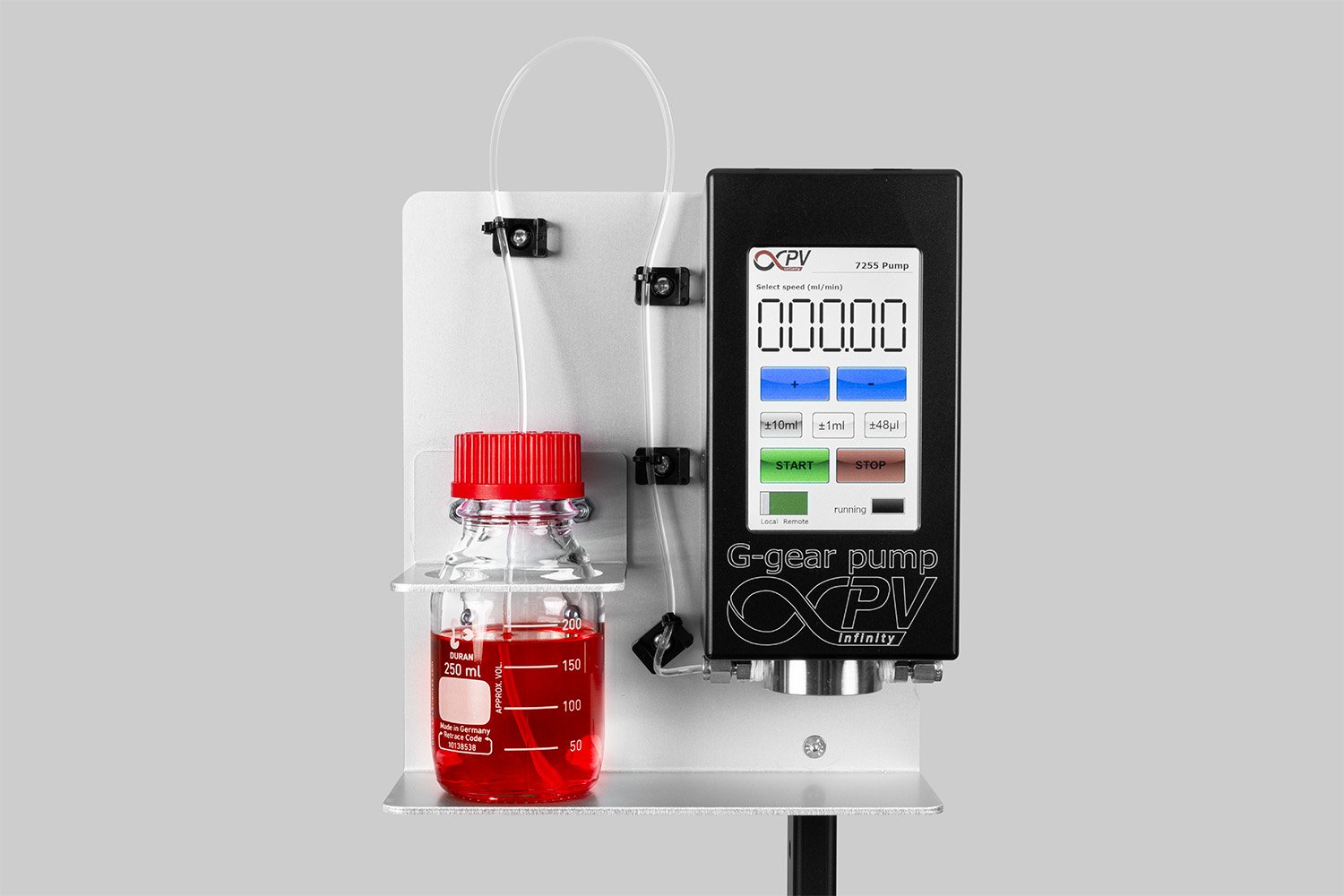
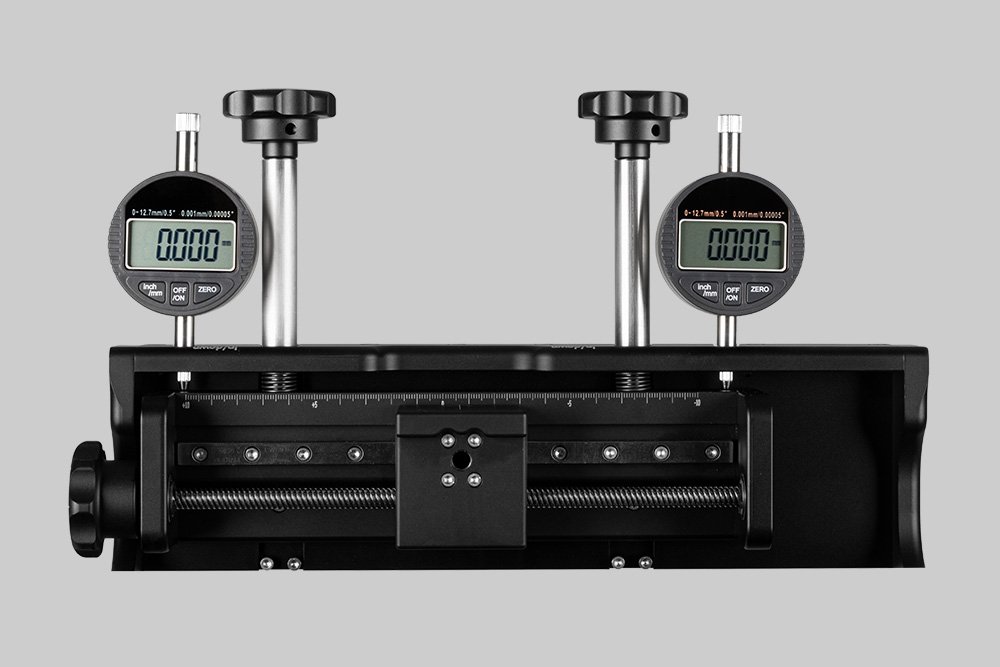
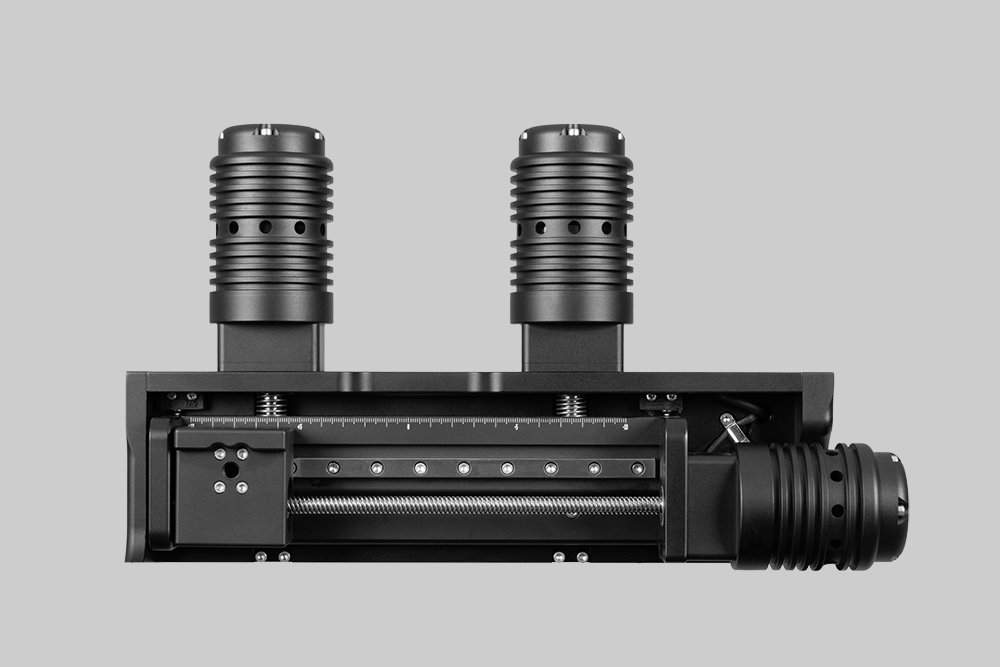




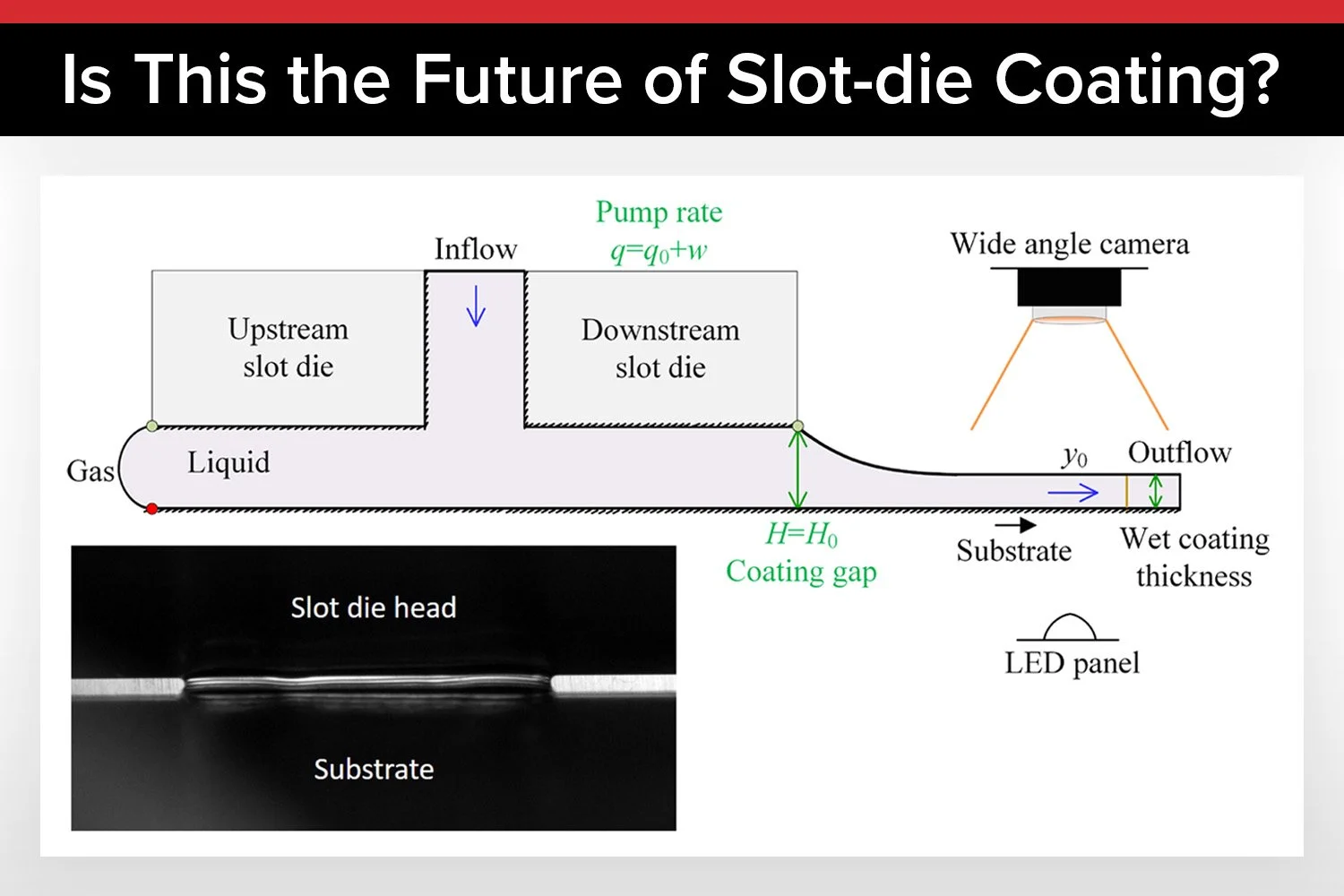






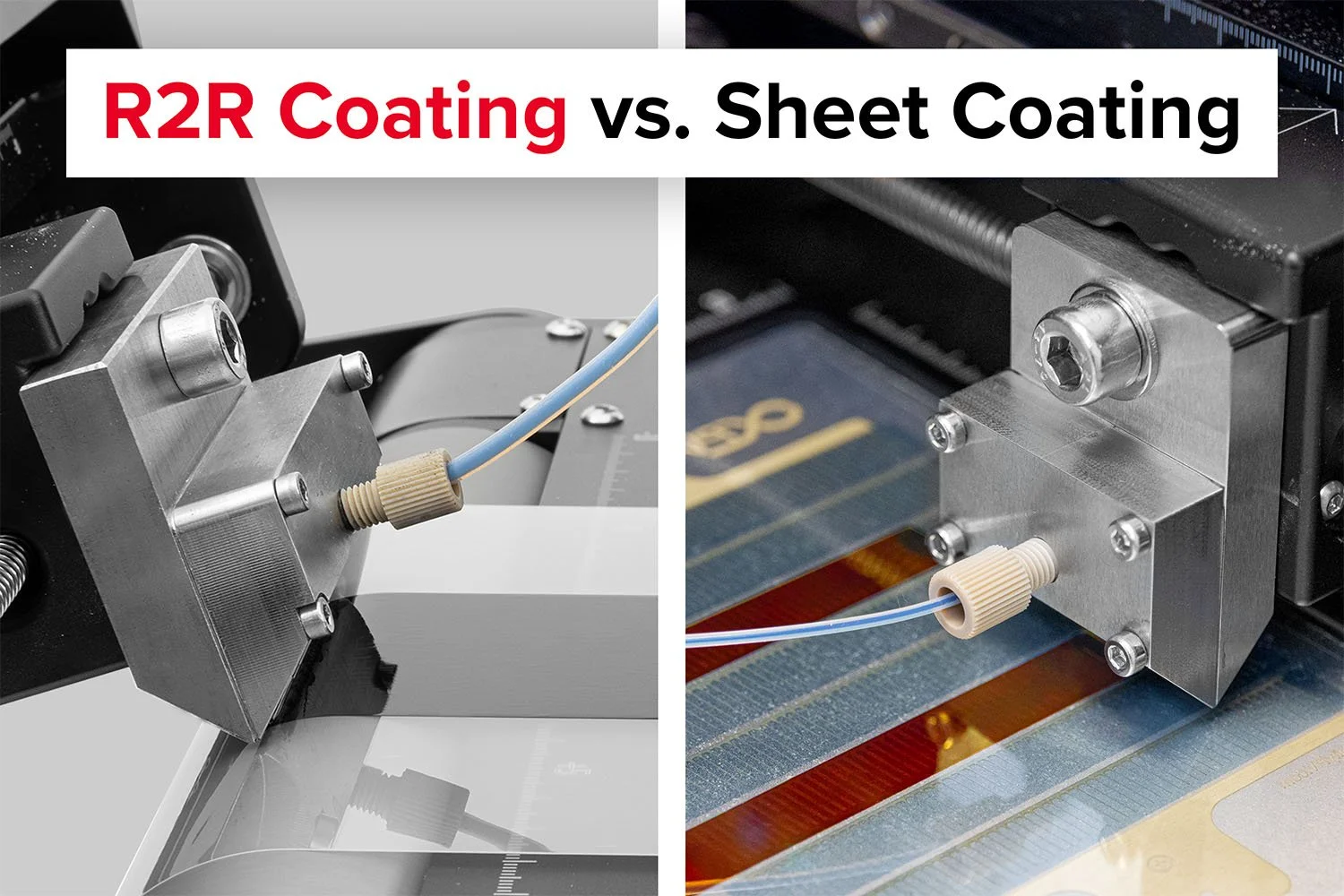













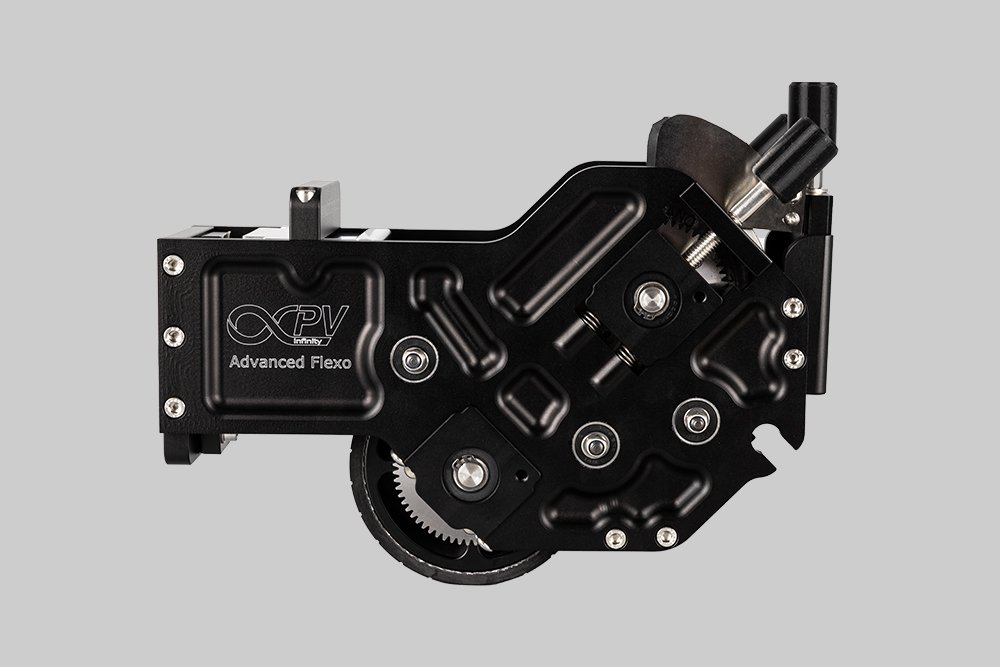

Probably the World’s Most Compact R2R Slot-die Coater: A compact, fully integrated roll-to-roll coating platform for laboratories, complete with a mounting system, anodized rollers, a syringe pump, a 65 mm stainless slot-die head and an infrared oven system—delivering unmatched precision and scalability.