Oral Thin Films: The Future of Supplements? Latest Research Into Nutraceutical Innovation
Are oral thin films the breakthrough nutraceuticals need?
In a world where convenience, precision, and bioavailability are increasingly prioritized in healthcare, one emerging technology stands out as a game-changer: oral thin films. The recent review, "The dawning era of oral thin films for nutraceutical delivery: From laboratory to clinic," published in Biotechnology Advances, explores how these innovative strips are poised to reshape the way we consume nutraceuticals. From overcoming digestive degradation to offering easier administration for vulnerable populations, oral thin films (OTFs) represent a major leap forward.
Nutraceuticals—products derived from food sources with extra health benefits—have long been plagued by problems related to stability, bioavailability, and user compliance. Traditional forms such as capsules and tablets often fall short, especially for people with swallowing difficulties. This review provides a comprehensive look at how OTFs not only solve many of these problems but also align well with modern-day expectations for personalized, effective health solutions. It brings together years of research, technological advances, and case studies to illustrate the real-world applicability of oral thin films and their future potential.
Key Highlights
Oral thin films dissolve quickly in the mouth, enabling fast absorption and bypassing the digestive system
Ideal for children, elderly, and patients with swallowing difficulties or chronic illness
Enhance bioavailability and reduce loss of nutrients due to liver metabolism
Provide precise, consistent dosing and improve patient adherence
Two major types are orodispersible and oromucosal films, each suited to different needs
Electrospinning and 3D printing allow for highly customizable and scalable production
Used to deliver a wide range of nutraceuticals including herbal extracts, vitamins, and probiotics
Quality by Design (QbD) approach ensures high product consistency and safety
Discover how lab-scale slot-die coating improves pharmaceutical and medical device development through precise, uniform coatings for testing and prototyping.
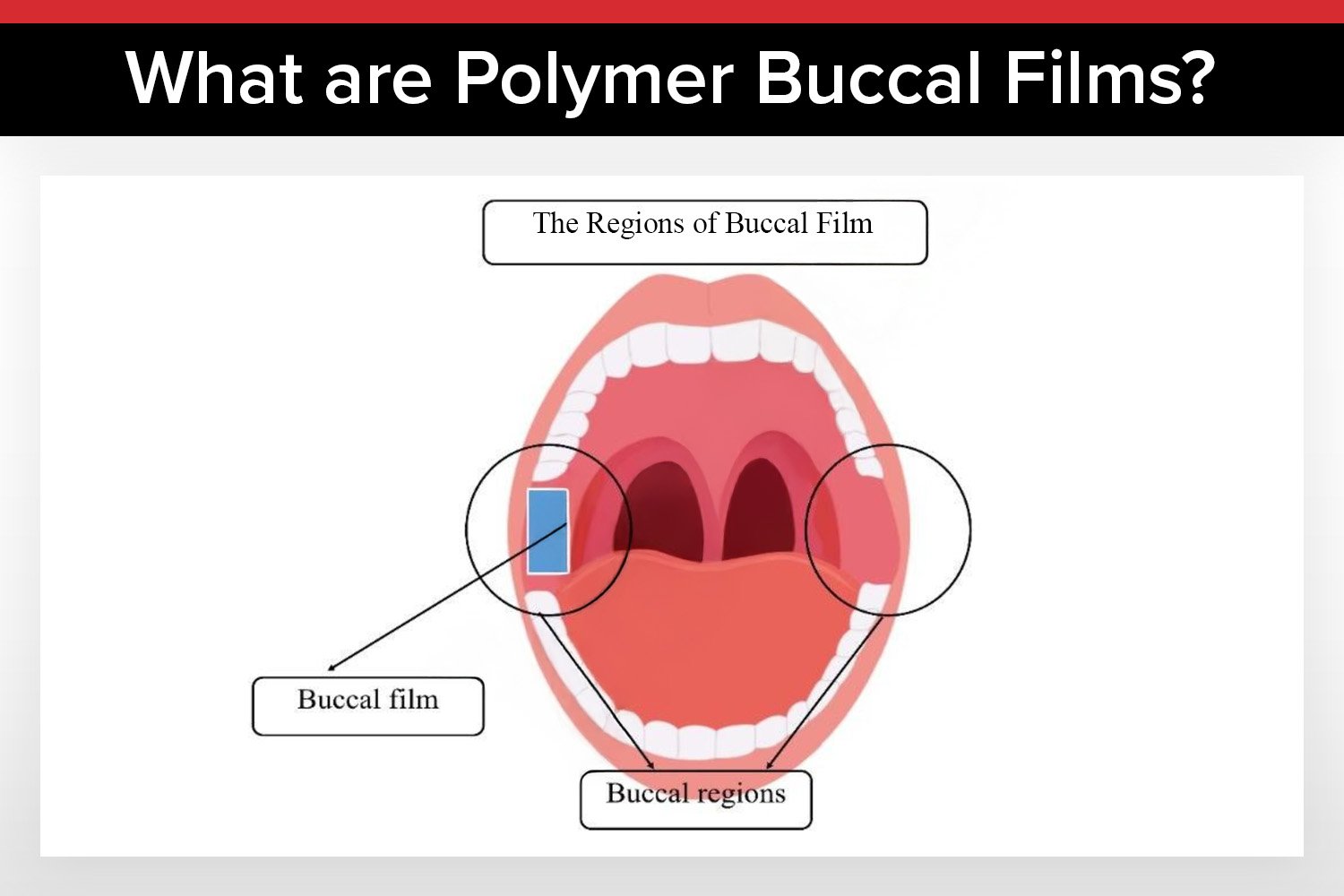
What Are Oral Thin Films and Why Do They Matter?
Oral thin films are ultra-thin, flexible polymer strips designed to deliver bioactive ingredients directly through the mucosal lining of the mouth. When placed on the tongue or against the inner cheek, these films rapidly disintegrate and allow the active ingredients to be absorbed either through the mucosal tissues or swallowed. This method significantly improves absorption efficiency and onset time compared to traditional oral dosage forms.
Unlike tablets or capsules that require water and can present swallowing challenges, especially among pediatric, geriatric, and special-needs populations, OTFs provide a convenient and comfortable alternative. They are also discreet and portable, which further supports user compliance. Their ability to bypass the gastrointestinal tract and first-pass liver metabolism ensures that a higher proportion of the active ingredient reaches systemic circulation, making them especially effective for compounds with low bioavailability.
The Significance of the Review: Why This Matters Now
The nutraceutical market is expanding rapidly, but its growth is hindered by persistent issues related to the delivery and absorption of bioactive compounds. Many of these compounds are unstable in the digestive system or require high doses to achieve therapeutic effects. This review addresses these critical issues head-on by showcasing OTFs as a versatile and efficient delivery platform.
The review is particularly timely, given the increasing consumer demand for non-invasive, effective, and user-friendly health solutions. It offers an in-depth analysis of how OTFs meet these demands through superior formulation science, innovative manufacturing techniques, and a deep understanding of patient needs. By compiling existing research, real-world applications, and market trends, the review positions oral thin films not as a future concept but as a viable and scalable solution already making its way into commercial and clinical settings.
Learn the complete process of creating uniform thin films using a slot-die coater.
Diving Into the Technology: How OTFs Work
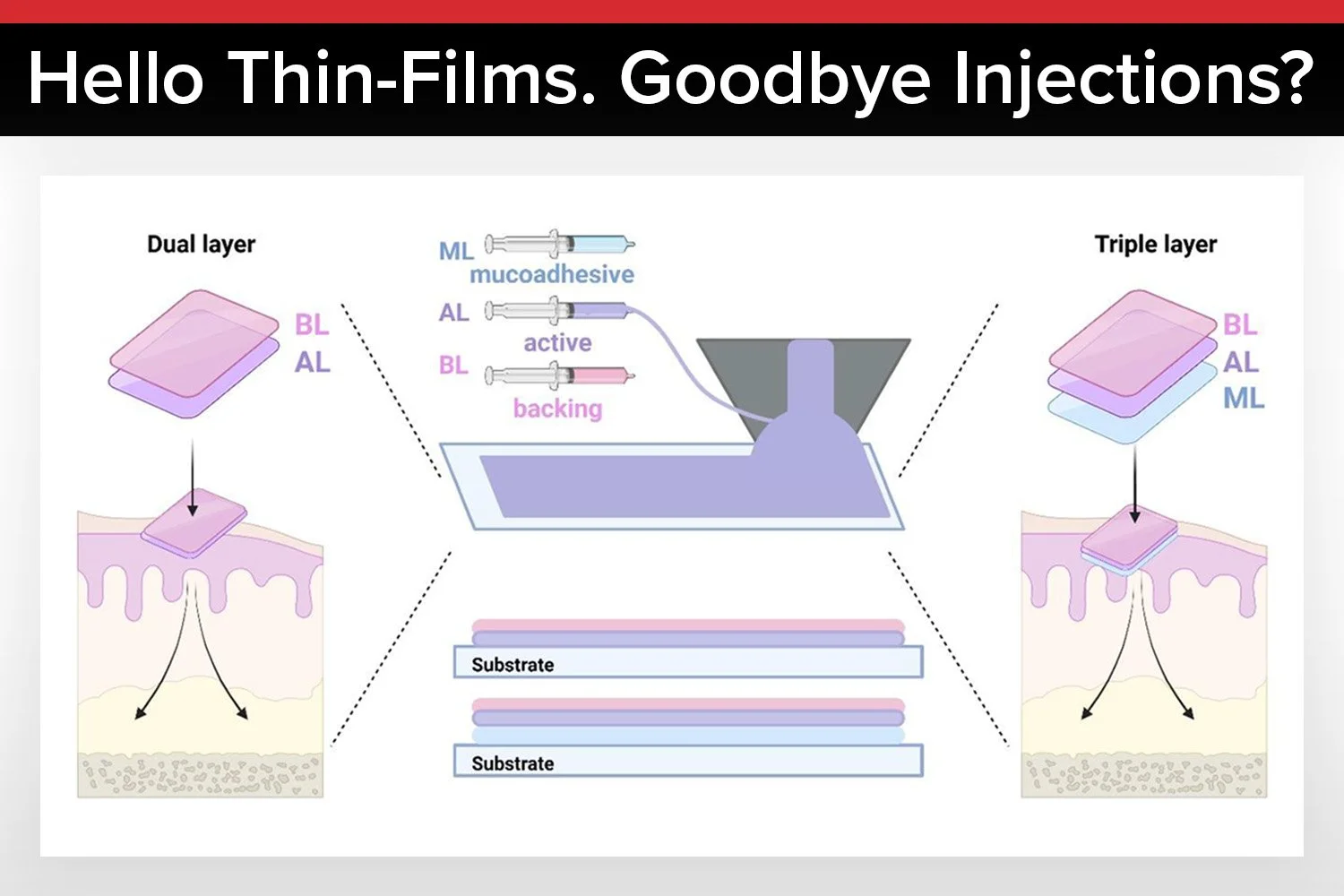
The functionality of oral thin films depends heavily on their design and composition. There are two main categories of OTFs: orodispersible films, which dissolve quickly in saliva and are absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, and oromucosal films, which adhere to the mucosa and release their contents for local or systemic absorption. Oromucosal films can be further classified based on their site of application, including buccal, sublingual, and palatal films.
Orodispersible films are ideal for rapid-release applications where fast onset of action is needed. These are commonly used for vitamins and other bioactives that do not require prolonged release. Oromucosal films, on the other hand, are designed for controlled release and targeted delivery. They adhere to the mucosal tissue and release their contents over a longer period, making them suitable for bioactives requiring sustained exposure.
Each type of film offers distinct advantages depending on the intended application, and their success depends on carefully selected polymers, excipients, and manufacturing techniques that support the desired release profile, stability, and patient experience.
Formulation Strategies: The Science of Excipients and Design
Formulating effective OTFs requires a nuanced understanding of both the bioactive compound and the excipients involved. Film-forming polymers serve as the structural backbone of the film and must offer both mechanical strength and rapid disintegration. Commonly used natural and synthetic polymers include hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), chitosan, pullulan, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA).
Plasticizers such as glycerol or polyethylene glycol are added to impart flexibility and reduce brittleness, which is essential for handling and packaging. Permeation enhancers improve the absorption of compounds that would otherwise struggle to penetrate the mucosal barrier. Additional ingredients like taste-masking agents, saliva stimulants, and sweeteners enhance the user experience and increase consumer compliance.
The review also emphasizes the importance of compatibility between the bioactive molecule and the chosen excipients. Factors like solubility, molecular weight, and ionic state significantly influence how well a compound can be incorporated into an OTF and how efficiently it will be absorbed.
Achieve pristine, contamination-free coatings with the Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater.
Innovative Manufacturing: From Casting to Printing
Traditional manufacturing methods such as solvent casting and hot-melt extrusion are well-established but have limitations including long drying times, sensitivity to heat, and batch-to-batch variability. To overcome these issues, the review highlights newer techniques like electrospinning and printing technologies.
Electrospinning allows the production of nanofibrous films with high surface area and porosity, which enhances both disintegration and bioavailability. It is especially useful for heat-sensitive ingredients. Inkjet and flexographic printing technologies enable precise dosing and are scalable for industrial production. These methods also support the development of multilayer films and personalized medicine applications by allowing digital customization of the dosage and composition.
Three-dimensional (3D) printing takes this even further by enabling the creation of structured, multi-polymer films with complex geometries and tailored release profiles. These advances not only improve the performance of OTFs but also reduce waste and increase manufacturing efficiency.
Real-World Applications: From Herbs to Probiotics
The review includes a wealth of case studies demonstrating the successful application of OTFs for a wide range of nutraceuticals. These include plant extracts like neem and ginkgo biloba, bioactive molecules such as curcumin and catechin, and functional ingredients like iron and vitamin C. In all cases, OTFs improved the bioavailability, stability, and user experience of the active ingredients.
For example, electrospun films loaded with ascorbic acid showed enhanced antioxidant activity and stability. Films incorporating herbal extracts such as pomegranate or neem demonstrated significant antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, while maintaining high consumer acceptability due to their taste-masked formulations. These practical examples underscore the versatility and effectiveness of oral thin films in real-world nutraceutical applications.
The Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater makes double-sided slot-die coating simple.
Future Outlook and Industry Potential
While the advantages of OTFs are compelling, the review also addresses the challenges that lie ahead. Regulatory pathways for nutraceutical OTFs are still under development, and standardization in quality control and clinical evaluation is lacking. Additionally, the high cost of advanced manufacturing techniques and the need for skilled labor present barriers to widespread adoption.
Despite these hurdles, the future looks promising. The growing interest in personalized nutrition, coupled with technological advancements in formulation and manufacturing, is likely to drive significant growth in the OTF market. There is also increasing collaboration between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies aimed at establishing clear guidelines and accelerating product development.
As more clinical studies validate the efficacy and safety of OTFs, and as consumer demand for convenient and effective health solutions continues to rise, oral thin films are well-positioned to become a mainstream delivery platform in the nutraceutical space.
Conclusion
Oral thin films represent a paradigm shift in how nutraceuticals are delivered. Their unique combination of rapid absorption, improved bioavailability, and user-friendly design addresses many of the limitations associated with traditional dosage forms. This review serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the current state and future potential of OTFs in the nutraceutical industry.
By compiling insights from formulation science, clinical research, and market analysis, the authors provide a compelling case for the adoption of oral thin films as a reliable, scalable, and consumer-preferred technology. As the industry continues to evolve, OTFs are not just an alternative but a leading contender for the future of nutraceutical delivery.
Authors
Ruchika
Nabab Khan
Shagun Sanjivv Dogra
Ankit Saneja
Get Professional Support for Your Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.
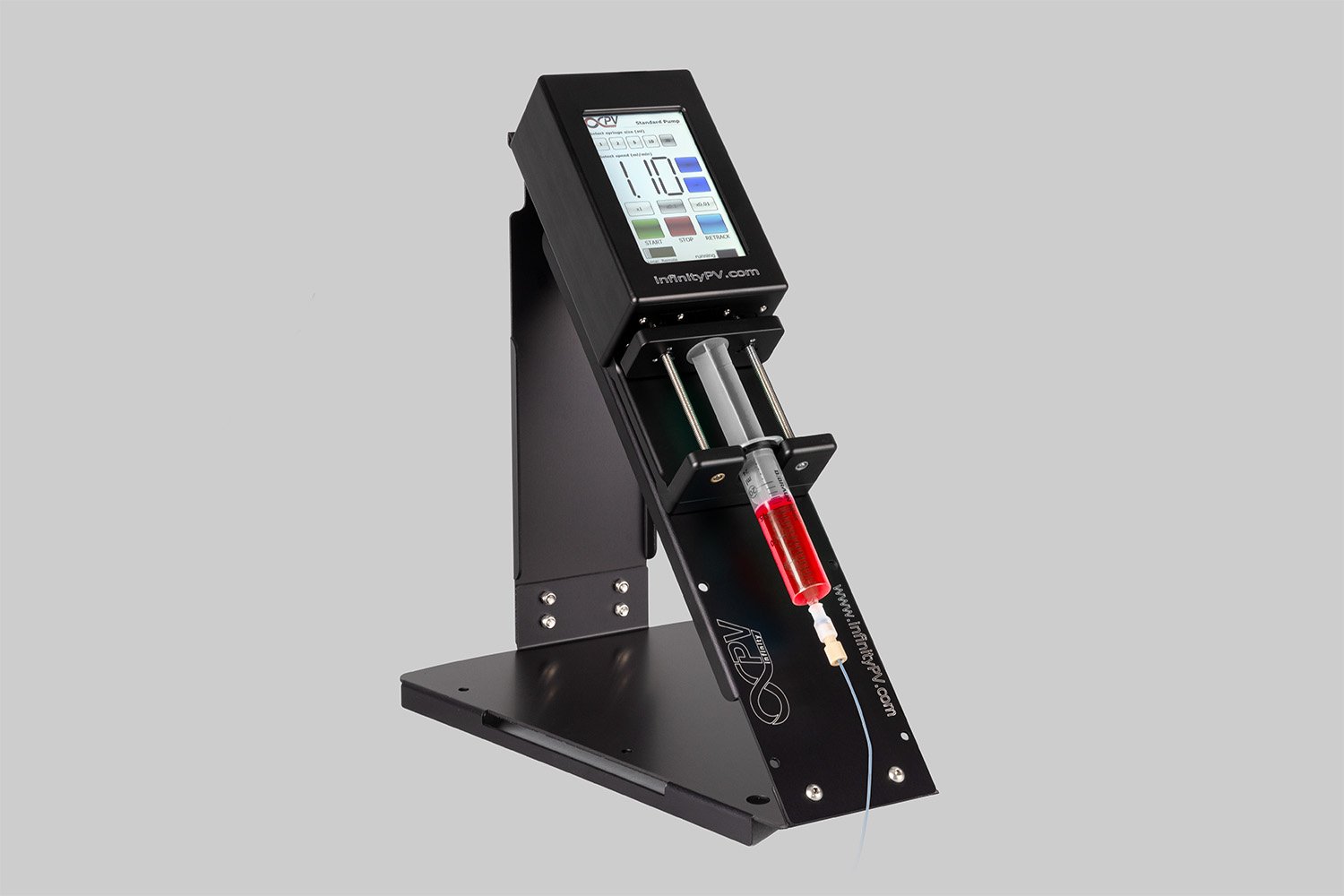
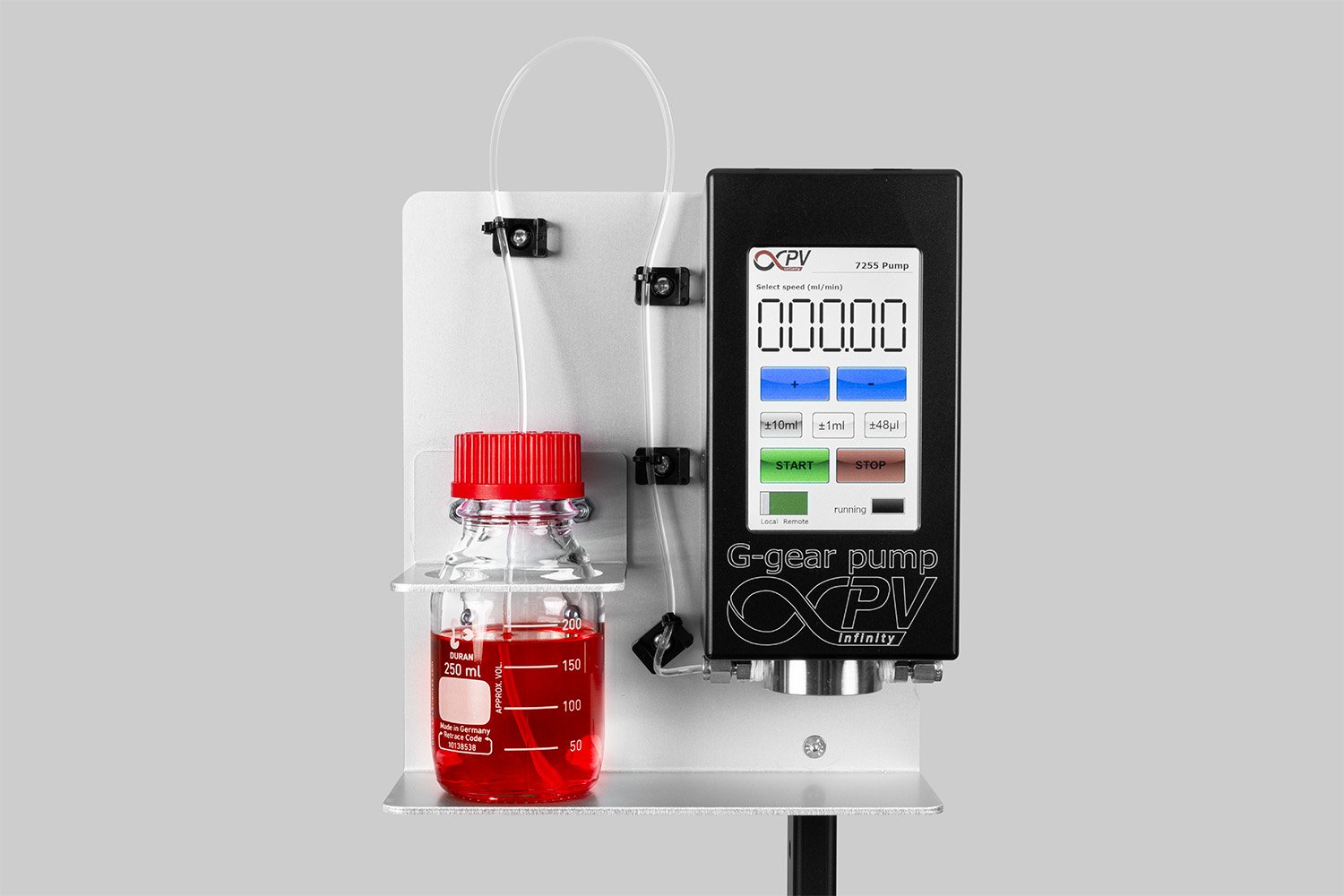
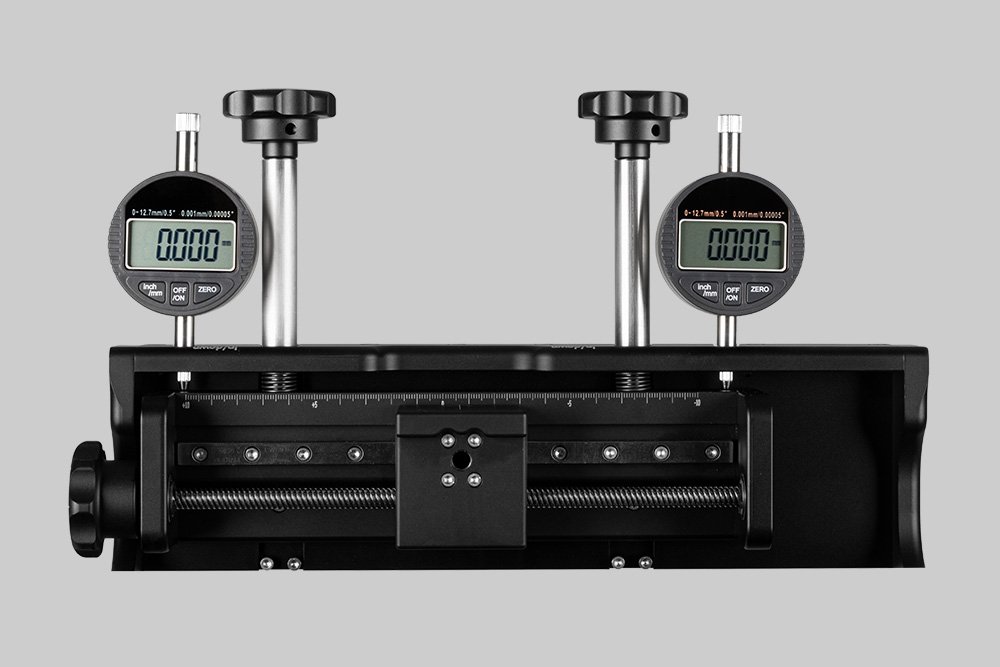
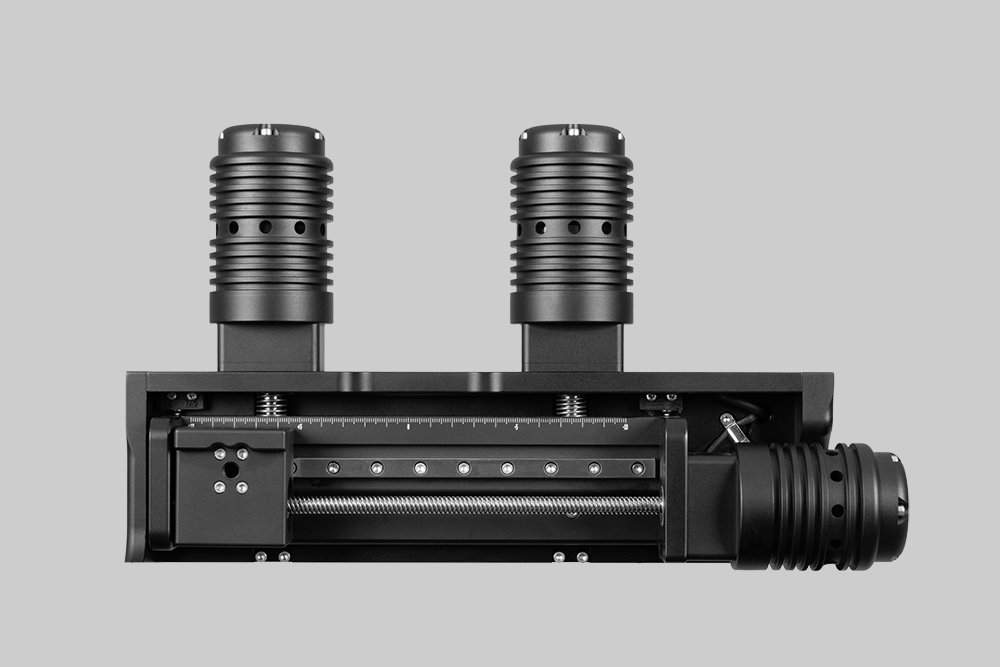






















Probably the World’s Most Compact R2R Slot-die Coater: A compact, fully integrated roll-to-roll coating platform for laboratories, complete with a mounting system, anodized rollers, a syringe pump, a 65 mm stainless slot-die head and an infrared oven system—delivering unmatched precision and scalability.