How to Achieve Perfect Battery Electrode Edges Using Slot-die Coating
Battery manufacturers face a persistent challenge: edge defects in slot-die coated electrodes. These bulges and ridges cause wrinkles, reduce yield, and limit how thick and how powerful batteries can be.
In a new study, Controlling Slot-Coating Edge Profiles of Battery Electrodes, researchers have now discovered that setting the gap between the slot-die and substrate equal to the wet coating thickness eliminates edge defects.
This rule could revolutionize battery production, enabling thicker, higher-energy electrodes without the usual flaws.
What You Need to Know
Making batteries involves coating a slurry onto metal foils to create electrodes. But the edges of these coatings often bulge or become uneven, causing defects that waste material and reduce performance.
Researchers have found that setting the gap between the slot-die and the foil equal to the thickness of the wet coating eliminates edge defects.
The findings allow battery makers to produce thicker, higher-energy electrodes without the usual flaws. This could lead to better batteries for electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage — with less waste and higher quality.
Slot-die coating is a critical step in manufacturing high-performance thin-film batteries.
The Technology Behind the Breakthrough: Slot-Die Coating Explained
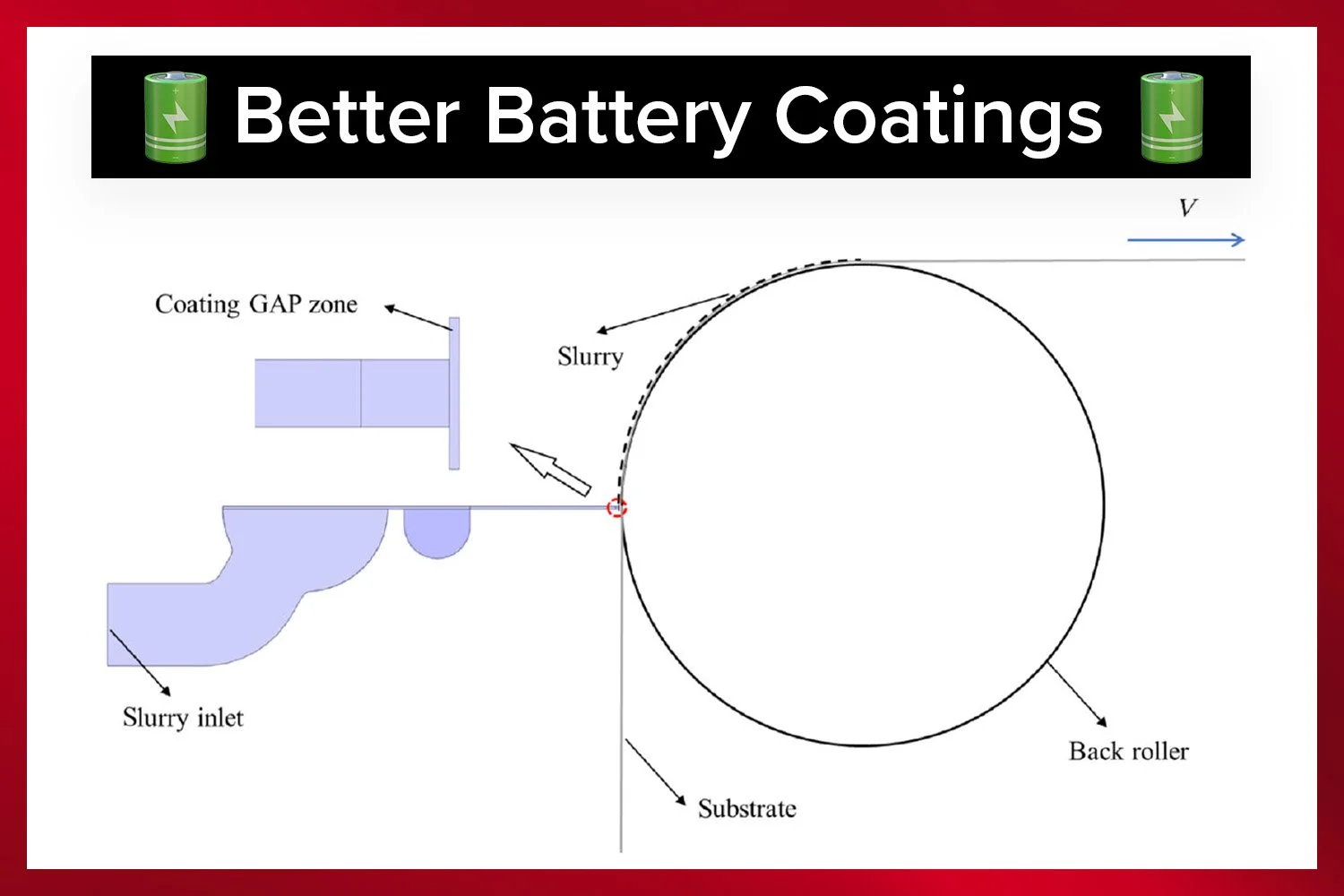
Slot-die coating is the industry standard for applying electrode slurries to metal foils. The process is precise and scalable, but edge defects have remained a stubborn issue. These defects, bulges or ridges at the edges of the coating, cause wrinkles during drying, leading to rejected batches and wasted material. The problem worsens with thicker coatings, which are essential for higher-energy batteries.
Traditionally, manufacturers have relied on trial and error to address edge defects, adjusting parameters like coating speed or slurry viscosity.
But this approach is inefficient and unreliable.
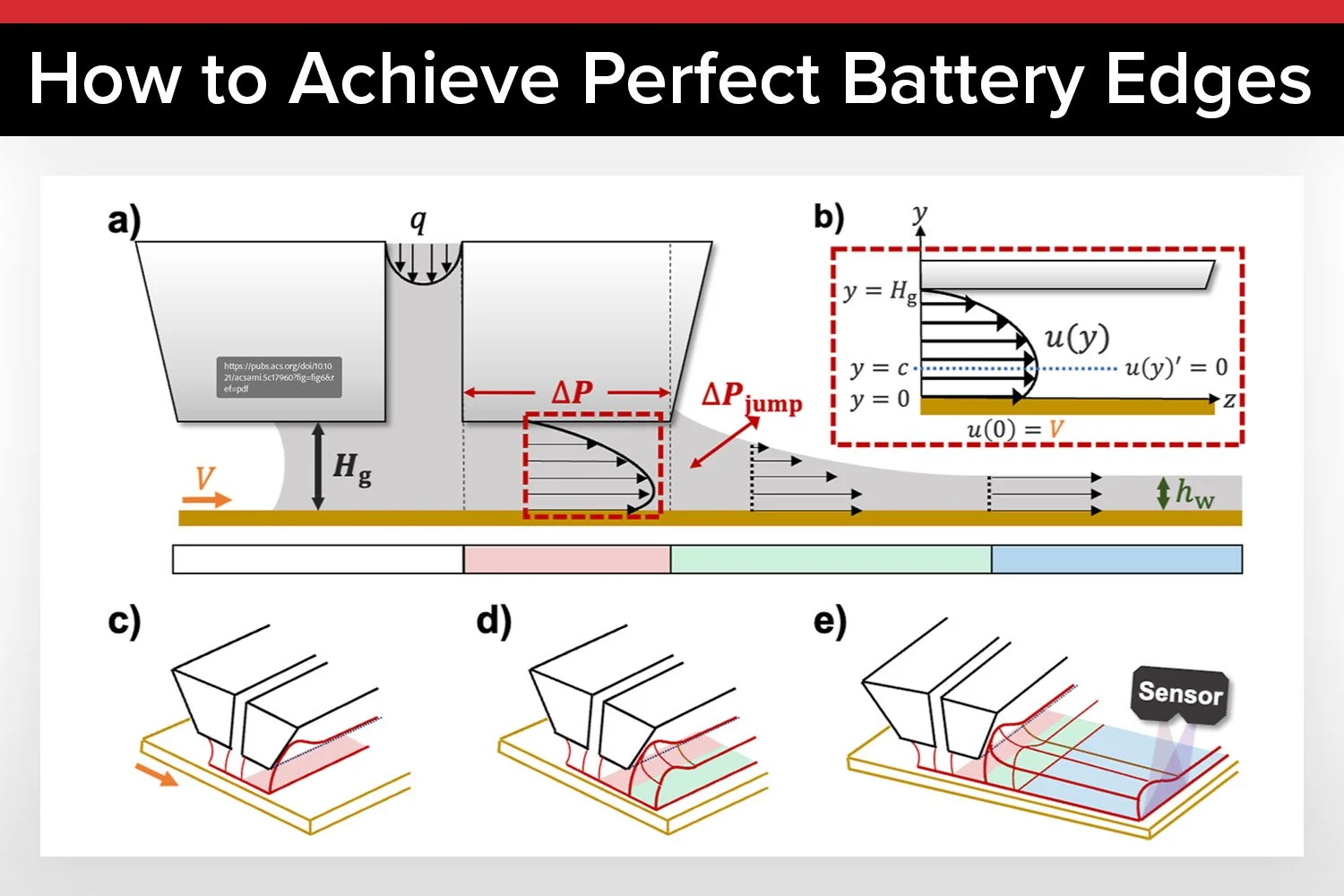
The new study changes that by providing a clear, actionable guideline: set the gap between the slot-die and the substrate equal to the wet coating thickness. This gap-to-thickness ratio of one ensures smooth, defect-free edges, eliminating much of the guesswork in the process.
The Impact of Edge Control
Edge defects are more than a minor annoyance. In high-volume production, even small increases in reject rates can translate to millions in lost revenue. For electric vehicle batteries, where thick electrodes are essential for higher energy density, edge control is a make-or-break factor.
The study’s most practical finding is simple yet powerful.
When the gap between the slot-die and the substrate equals the wet coating thickness, edge quality is optimal. This rule works across different materials and settings, giving manufacturers a reliable way to produce high-quality electrodes.
Beyond batteries, the principles uncovered here apply to any industry using slot-die coating, from solar cells to printed electronics. By understanding the interplay of pressure, capillary forces, and leveling flows, engineers can predict and prevent edge defects before they occur.
Achieve consistent slurry coatings with ease using the Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater.
A Closer Look at the Methods
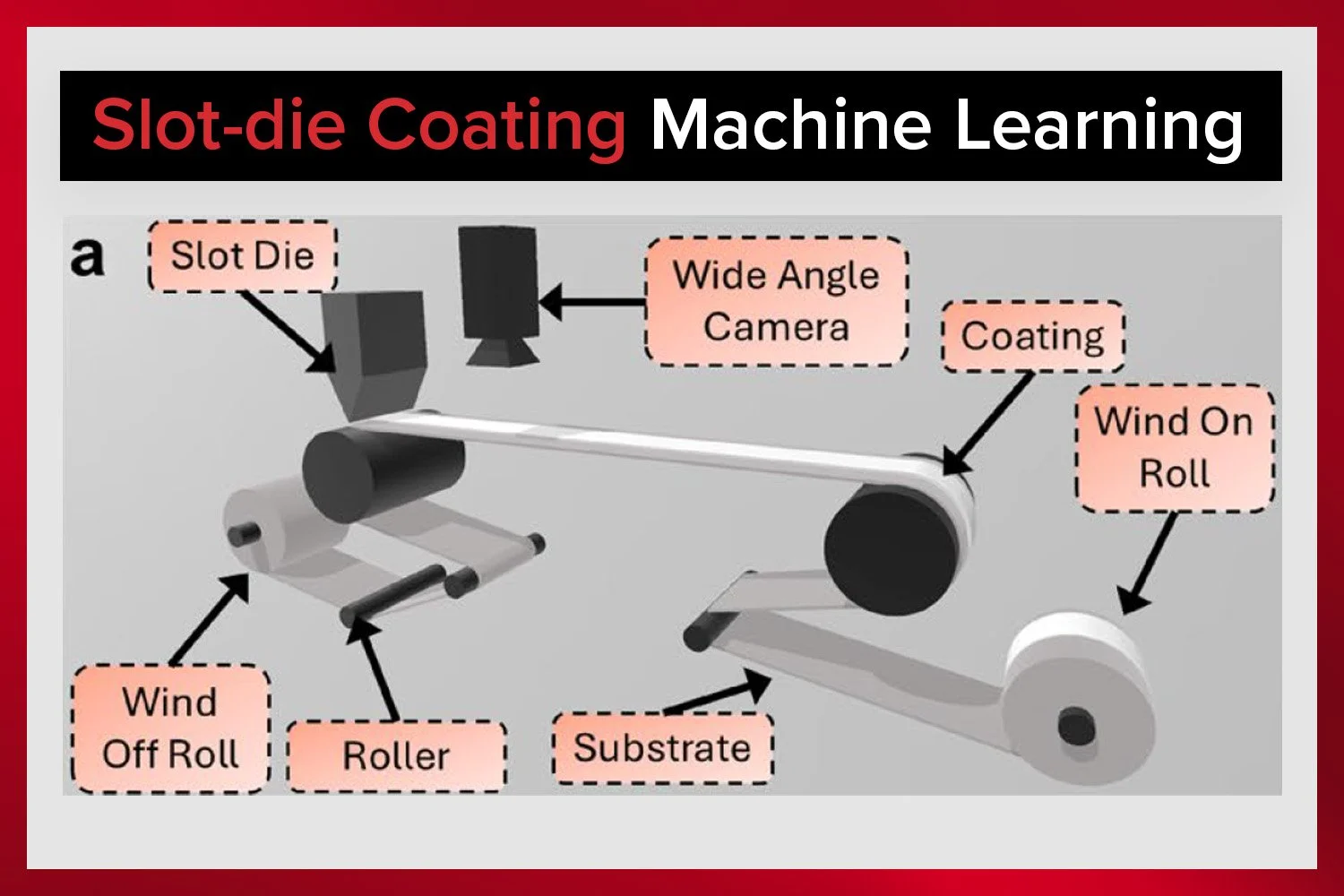
The researchers conducted over five hundred experiments using a lab-scale roll-to-roll slot-coating system equipped with a high-resolution laser sensor. They varied process conditions, including slot-die configurations, slurry properties, and substrate speed, to explore how each factor affects edge profiles.
An automated system was developed to analyze edge profiles consistently, even for irregular shapes. This system uses segmented regression to define edge width and a damped oscillatory model to extract the true edge slope, accounting for surface tension and viscosity.
To understand the physical mechanisms behind edge formation, the team developed a visco-capillary model. This model simulates the flow within the coating bead, predicting pressure drops and capillary pressure jumps. It revealed that edge formation is driven by pressure distribution and downstream leveling flows.
Machine learning played a crucial role in the analysis. Using XGBoost and SHAP analysis, the researchers identified the gap-to-thickness ratio as the dominant factor influencing edge quality. This insight provides manufacturers with a clear guideline: set the gap-to-thickness ratio to one for optimal results.
The Future of Battery Manufacturing
The findings of this study have far-reaching implications. With the gap-to-thickness ratio rule, manufacturers can now produce thick electrodes without fear of edge defects. This is a major step toward higher-energy batteries for electric vehicles and grid storage.
The principles uncovered here also apply to other industries using slot-die coating. From solar cells to printed electronics, controlling edge profiles will lead to higher quality products and more efficient manufacturing.
The study highlights the growing role of data and automation in modern manufacturing. By using machine learning to analyze complex datasets, the researchers identified patterns that would have been difficult to discern through traditional methods. This data-driven approach is likely to become increasingly important as processes grow more complex.
Looking ahead, challenges remain, such as understanding edge width variability and optimizing high-speed coating. But the study represents a major leap forward, providing a clear path to higher quality, lower waste, and more scalable battery production.
Your coating process is only as good as the slot-die head that delivers it. Our guide helps you evaluate your needs and choose the right slot-die head for optimal quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Read the selection guide here.
Conclusion: A New Standard for Battery Electrode Coating
The study Controlling Slot-Coating Edge Profiles of Battery Electrodes shows that by setting the gap between the slot-die and the substrate equal to the wet coating thickness, manufacturers can eliminate edge defects and produce thicker, higher-energy electrodes.
For the battery industry, this means fewer rejects, higher yields, and a competitive edge in the race for better performance. For the rest of us, it’s a step closer to the high-performance batteries that will power the next generation of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
Authors
Jihwan Yoon
Kyengmin Min
Jisoo Song
Jaewook Nam
Get Professional Support for Your Battery Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.

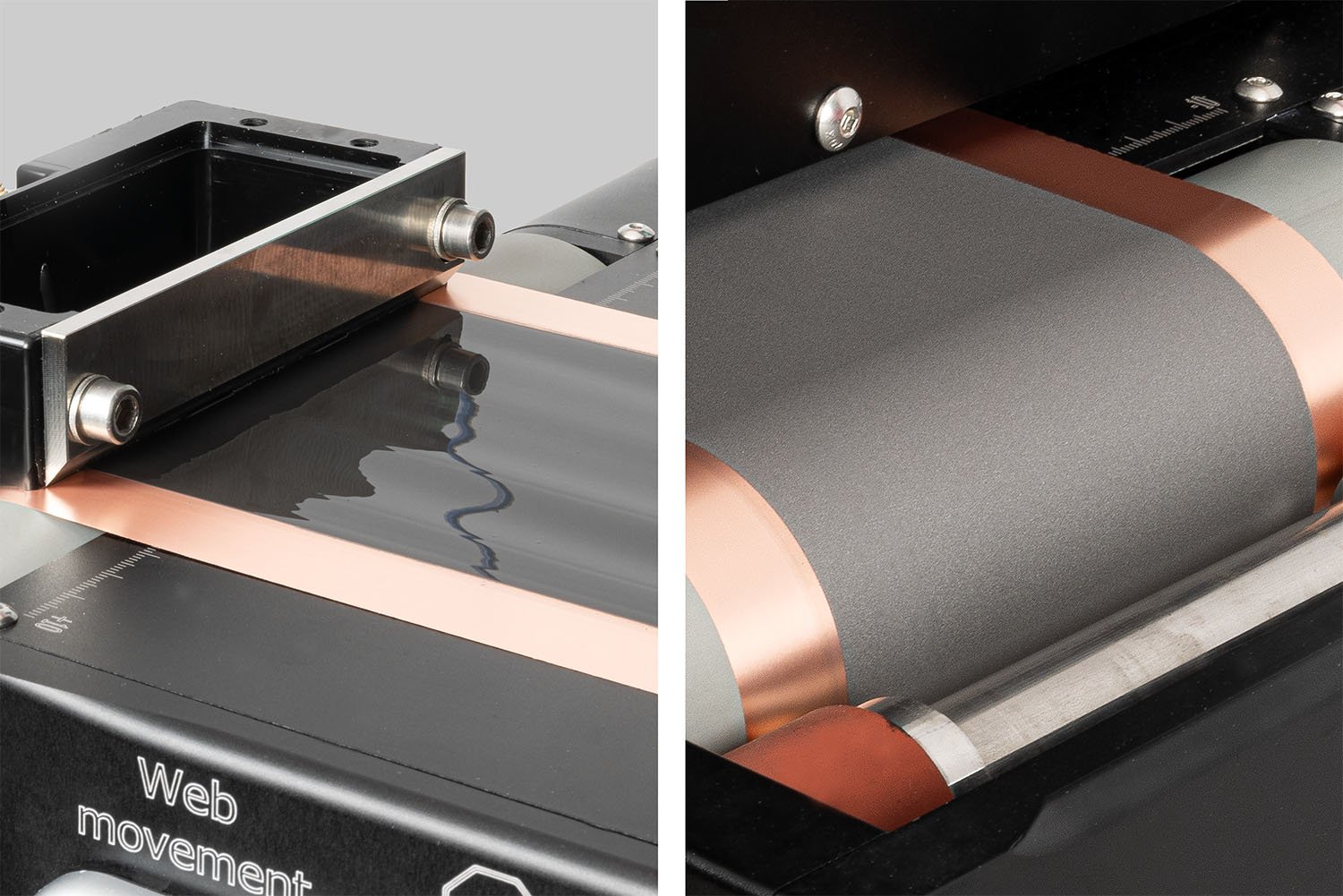



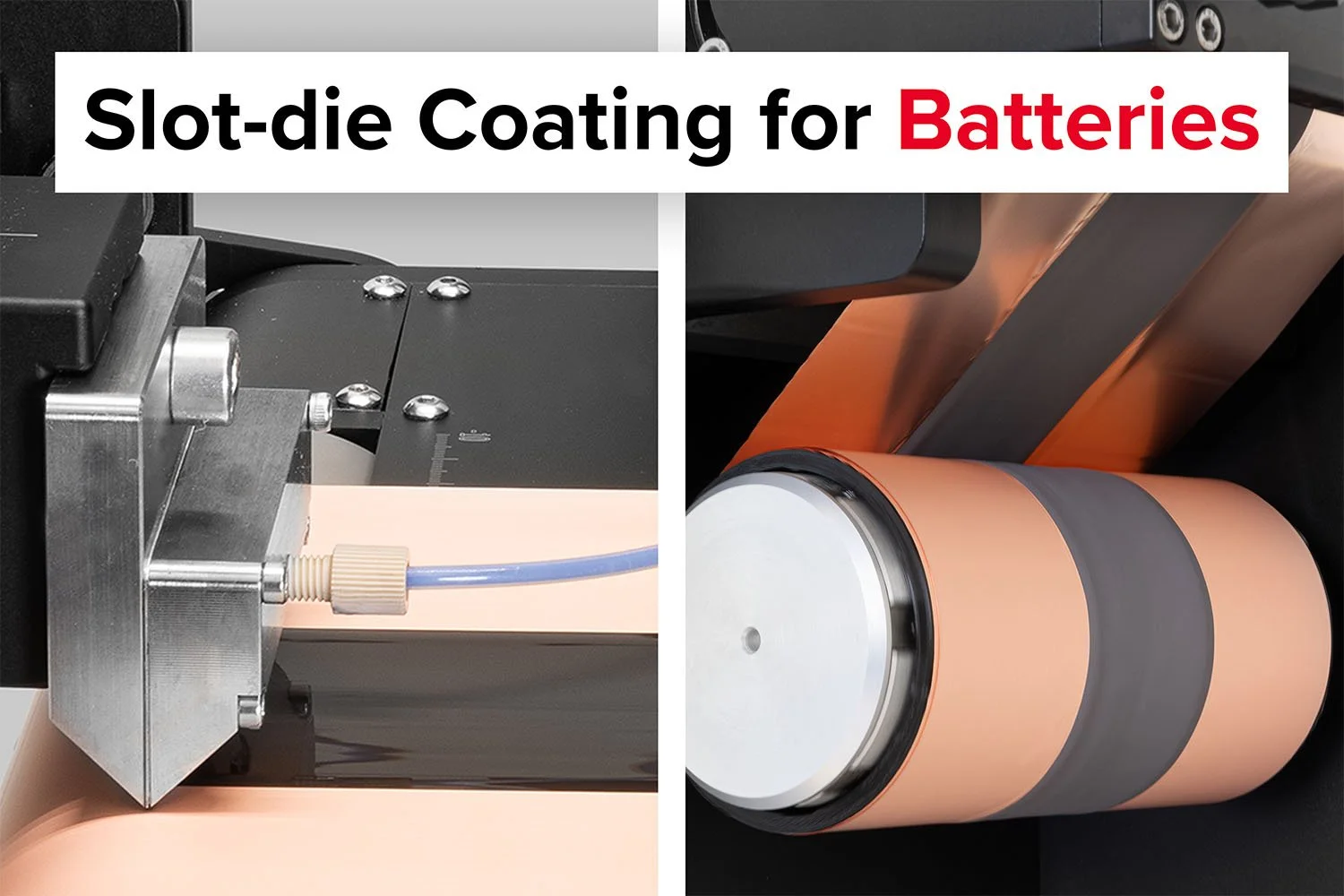











The SDC Battery Coater Pro is specifically designed for researchers dedicated to developing and optimizing battery materials. It facilitates a seamless transition from research to commercialization. View video.