How Polymer Buccal Films Improve Drug Delivery for Patients
Imagine taking your medication without swallowing a single pill. No water needed, no risk of choking, and no stomach upset. Instead, you place a thin, flexible film inside your cheek, where it gently dissolves, releasing medicine directly into your bloodstream.
This is the reality of polymer buccal films, an innovative drug delivery system that’s gaining traction in modern healthcare.
A recent review titled "Polymer Buccal Films as Innovative Approach in Drug Delivery Systems: A Review", published in Materials Research Express, explores how these films work and why they’re becoming a preferred alternative to traditional oral medications. This review highlights how buccal films offer a patient-friendly, efficient, and targeted way to deliver drugs, particularly for those who struggle with swallowing pills.
But why does this matter now?
Traditional oral drugs often face challenges like low bioavailability, gastrointestinal irritation, and poor patient compliance, especially among children and the elderly. Buccal films address these issues by delivering medication directly through the buccal mucosa, bypassing the digestive system and liver metabolism. This means faster absorption, fewer side effects, and better treatment outcomes.
What You Need to Know
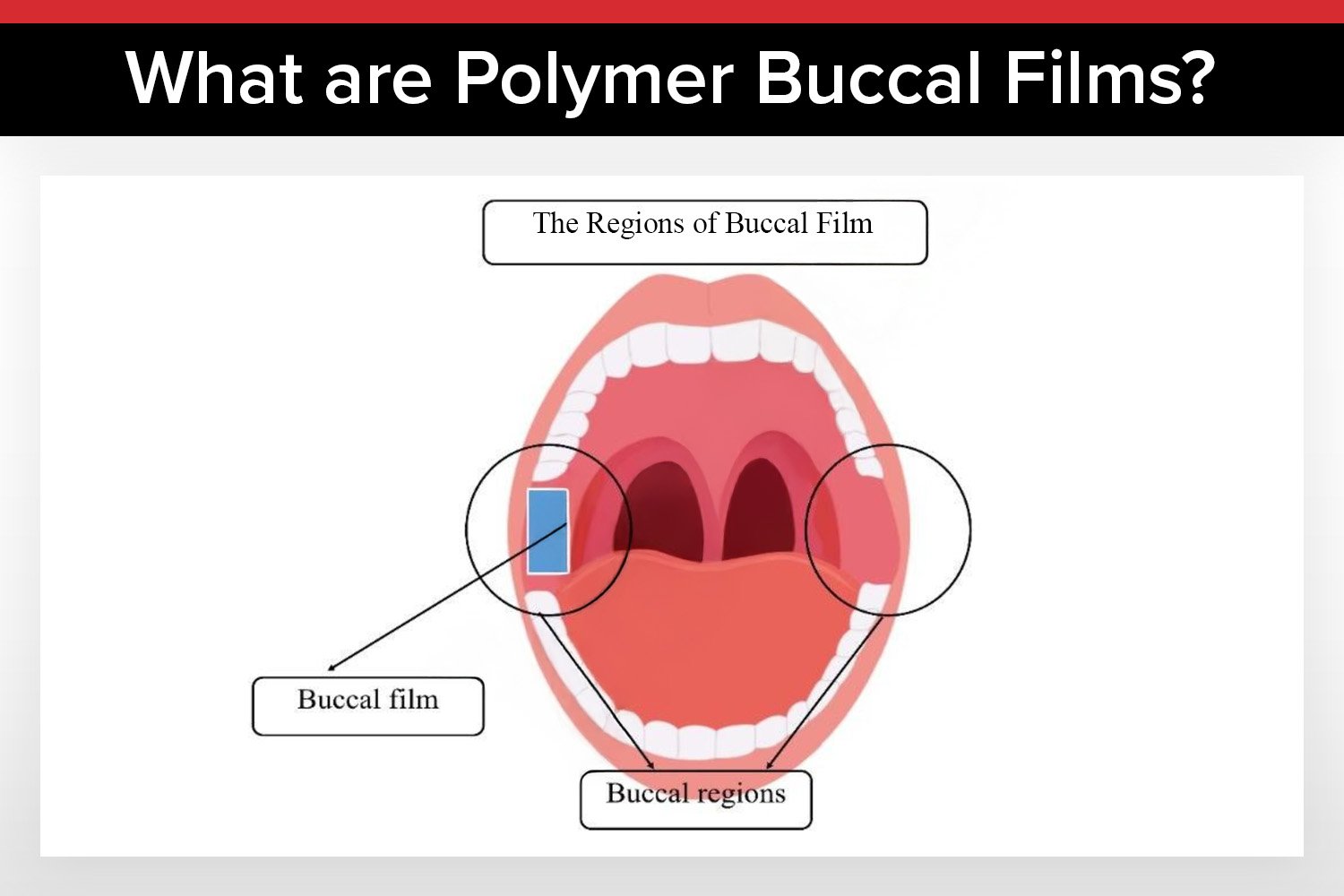
Polymer buccal films are thin patches that stick to the inside of your cheek, dissolving to release medication directly into your bloodstream.
Unlike traditional pills, they bypass the stomach, making them faster, more efficient, and easier to use, especially for those who struggle with swallowing.
The review explains how these films are made, their benefits, and why they could become a standard in drug delivery
What Are Polymer Buccal Films?
A New Approach to Drug Delivery
Buccal drug delivery involves placing medication inside the cheek, where it dissolves and enters the bloodstream directly through the buccal mucosa. Unlike traditional pills, which must survive the stomach’s acidic environment, buccal films bypass the digestive system entirely, leading to higher drug bioavailability and fewer side effects.
This method is particularly beneficial for patients who struggle with swallowing, such as children, the elderly, or those with conditions like dysphagia. It also offers a more comfortable and convenient alternative to injections or liquid medications.
The Role of Polymers
Polymers are the backbone of buccal films, determining their strength, flexibility, and drug-release properties. The review categorizes polymers into three main types:
Natural polymers, like chitosan and sodium alginate, are biocompatible and biodegradable, making them safe for long-term use. Chitosan, for example, has strong mucoadhesive properties, helping the film stay in place for better drug absorption. However, natural polymers can sometimes lack mechanical strength.
Synthetic polymers, such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and Eudragit, offer superior durability and controlled drug release. These polymers can be engineered to meet specific therapeutic needs, but they may raise environmental concerns and cost more to produce.
Smart polymers are the future of buccal films. These materials respond to environmental triggers, like changes in pH or temperature, allowing for dynamic drug release. For instance, a smart polymer film might release medication only when it detects an acidic environment, ensuring targeted delivery. While still emerging, smart polymers hold significant promise for personalized medicine.
Why Buccal Films Are a Game-Changer
Buccal films represent a shift toward patient-centric healthcare. Their ease of use, targeted delivery, and flexible dosing make them a standout innovation in drug delivery.
For patients, buccal films offer convenience and comfort. There’s no need to swallow anything, and the films can be designed to dissolve quickly or release medication over time. This flexibility is especially beneficial for chronic conditions requiring consistent medication.
For healthcare providers, buccal films provide a reliable and efficient way to administer drugs. Their ability to bypass the digestive system and liver metabolism means that lower doses may achieve the same therapeutic effect, reducing side effects.
For the pharmaceutical industry, buccal films open up new possibilities for drug formulation and delivery. The ability to use different polymers and fabrication techniques allows for a high degree of customization, making it possible to tailor treatments to individual patient needs.
Learn the complete process of creating uniform thin films using a slot-die coater.
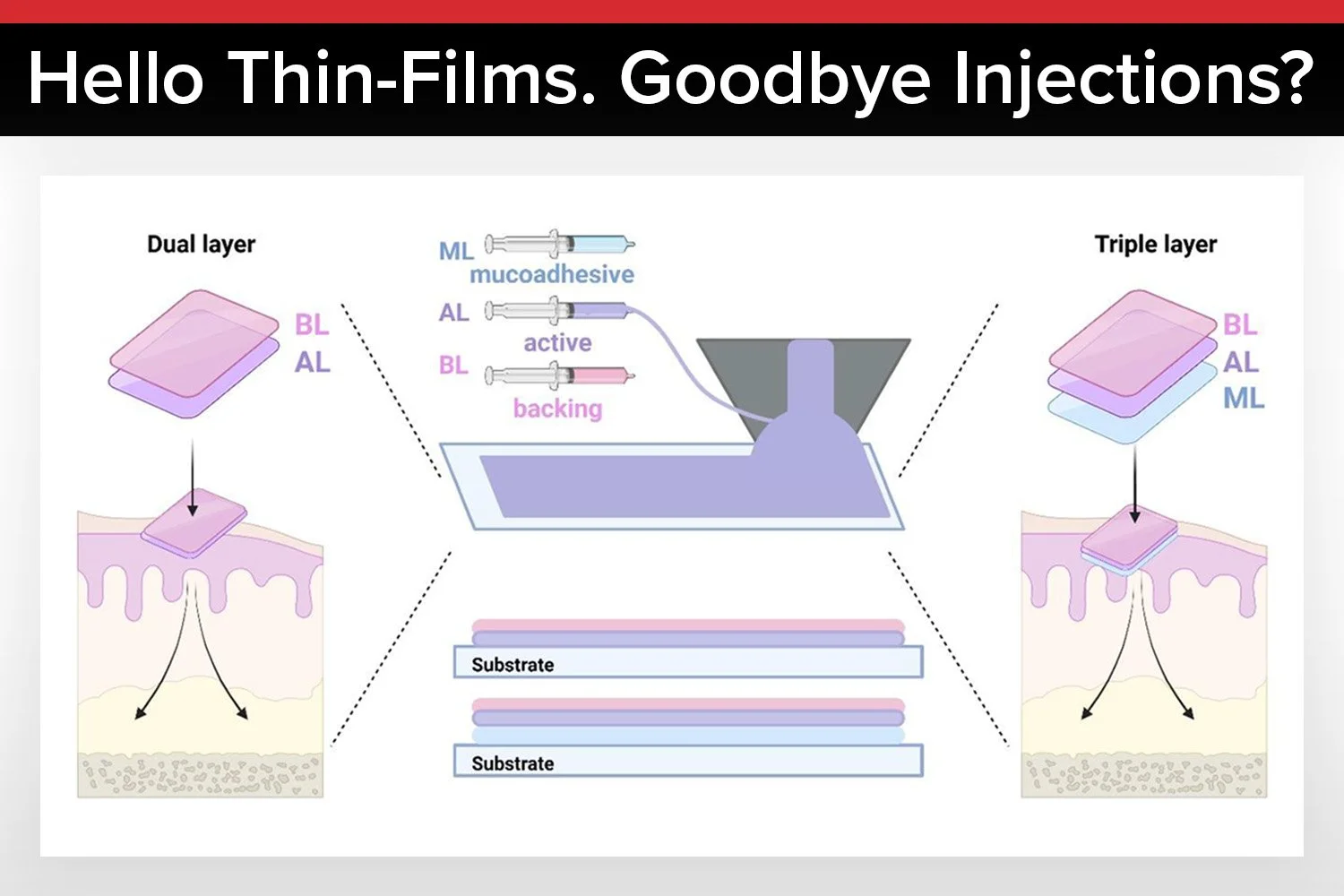
How Are Buccal Films Made?
The fabrication of buccal films combines material science and pharmaceutical engineering. The review outlines several key methods, each with its own advantages and challenges.
Solvent casting is a simple and cost-effective method where polymers and drugs are dissolved in a solvent, cast into a thin layer, and dried to form a film. While easy to perform, solvent casting can leave residues and offers limited control over film uniformity.
Hot melt extrusion melts polymers and drugs together, mixes them, and extrudes the mixture into a film. Hot melt extrusion is eco-friendly and safe, making it ideal for thermosensitive drugs. However, it requires precise temperature control and may not suit all polymers.
Electrospinning uses an electric field to draw polymer-drug solutions into ultrafine fibers, creating highly porous films. These films allow for rapid drug release and excellent mucoadhesion. However, the process is complex and may be difficult to scale for mass production.
3D printing enables the creation of custom-shaped films tailored to individual patient needs. This technology could revolutionize personalized medicine, though high equipment costs and regulatory hurdles remain challenges.
Slot-die coating is a precise method for depositing polymer-drug solutions onto a moving substrate. It offers uniform film thickness and is highly scalable for industrial production, though it requires specialized equipment.
Learn why modular R2R coaters are ideal for functional thin-film research.
The Science Behind Mucoadhesion
Mucoadhesion, the ability of a buccal film to stick to the mucosal surface, is essential for its effectiveness. Without strong adhesion, the film could be washed away by saliva, rendering it useless.
How Mucoadhesion Works
Mucoadhesion occurs in two stages. First, the film makes contact with the moist mucosal surface. Second, moisture activates the polymer, allowing it to bond with the mucus layer through hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, and ionic interactions.
Polymers like chitosan, which have a positive charge, interact strongly with the negatively charged buccal mucosa, enhancing adhesion. Synthetic polymers can also be engineered to improve mucoadhesive properties.
Factors Affecting Mucoadhesion
Several factors influence mucoadhesion, including the type of polymer, molecular weight, plasticizers, and crosslinking. Higher molecular weight polymers penetrate deeper into the mucus layer, while plasticizers improve flexibility but must be balanced to avoid over-softening the film.
Crosslinking can enhance mechanical strength but may reduce mucoadhesion if overdone. The goal is to create a film that is strong yet flexible, ensuring it stays in place for optimal drug delivery.
Why Mucoadhesion Matters
Strong mucoadhesion ensures the film stays in contact with the mucosa long enough for the drug to be absorbed. This prolongs drug delivery, improves patient comfort, and enhances bioavailability by minimizing drug loss due to saliva washout.
Discover how lab-scale slot-die coating improves pharmaceutical and medical device development through precise, uniform coatings for testing and prototyping.
Permeability: Ensuring Drugs Reach Their Target
For a buccal film to be effective, the drug must permeate the mucosal barrier and enter the bloodstream. Several factors influence permeability, from physiological conditions to film composition.
Physiological Factors
Saliva, mucosal thickness, and blood flow all affect drug absorption. The buccal area’s rich vascularization allows drugs to enter the bloodstream quickly, bypassing liver metabolism.
Film-Related Factors
Polymer type, drug properties, and permeation enhancers like tween-80 influence how easily drugs cross the mucosal barrier. Hydrophilic polymers release drugs faster, while hydrophobic polymers offer more controlled release.
Optimizing Permeability
Researchers are exploring strategies like nanoparticle encapsulation and stimuli-responsive polymers to enhance permeability and drug absorption.
Achieve pristine, contamination-free coatings with the Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater.
Conclusion: The Promise of Polymer Buccal Films
Polymer buccal films represent a patient-centric, efficient, and adaptable approach to drug delivery. This review by Fitri and colleagues provides a comprehensive roadmap for their development, highlighting their potential to transform medication.
From bypassing the digestive system to offering customizable and comfortable designs, buccal films address many limitations of traditional oral medications. As research advances, innovations like 3D printing and smart polymers could make these films even more effective.
For industries like roll-to-roll manufacturing, buccal films present an exciting opportunity to contribute to next-generation drug delivery systems. The future of medicine isn’t just about the drugs we take—it’s about how we take them, and buccal films are leading the way toward a smarter, more patient-friendly approach.
Authors of the Study
Tuty Fareyhynn Mohammed Fitri
Azlin Fazlina Osman
Sinar Arzuria Adnan
Heru Suryanto
Get Professional Support for Your Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.
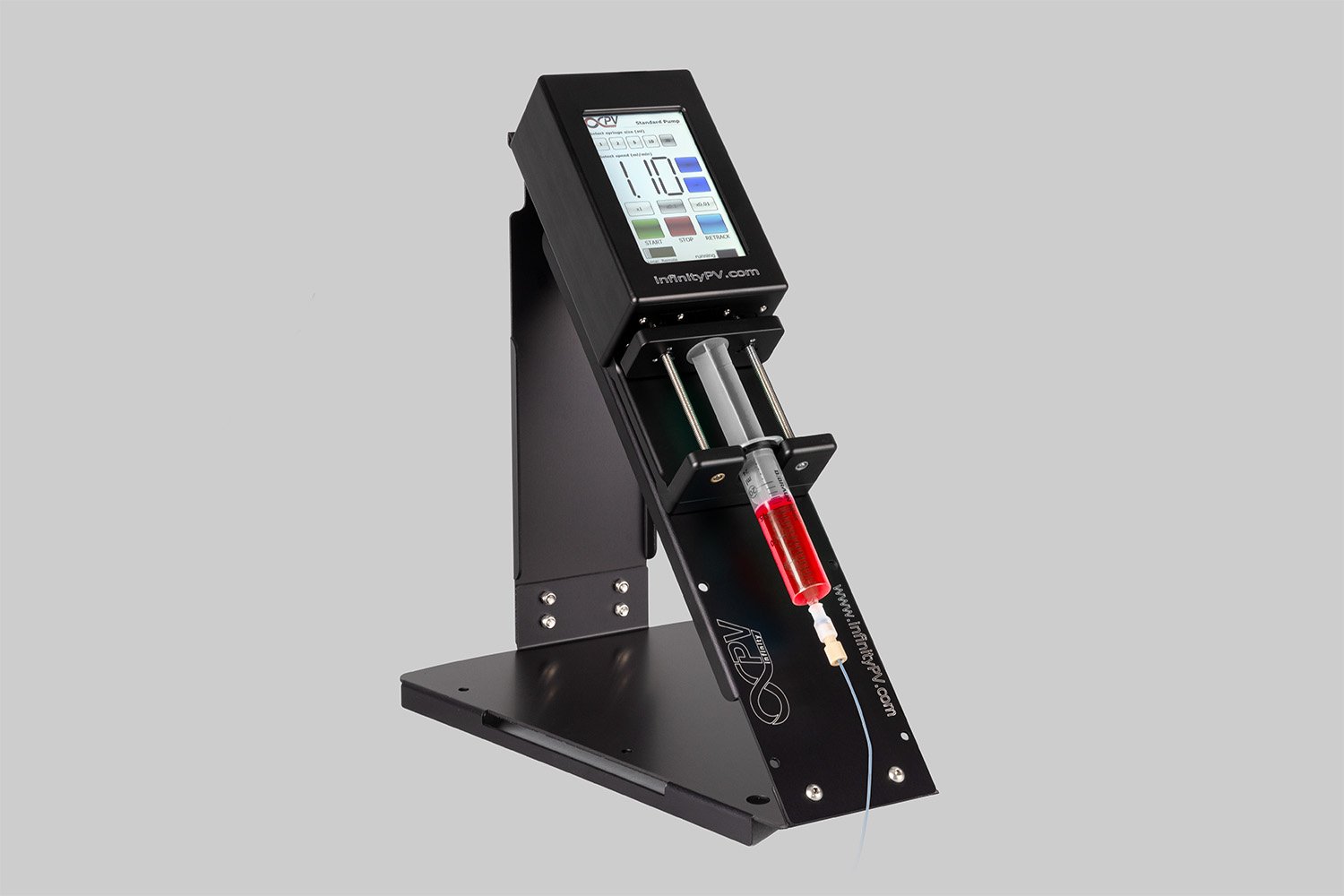






















Probably the World’s Most Compact R2R Slot-die Coater: A compact, fully integrated roll-to-roll coating platform for laboratories, complete with a mounting system, anodized rollers, a syringe pump, a 65 mm stainless slot-die head and an infrared oven system—delivering unmatched precision and scalability.