Could Thin Films Replace Injections? Layer-by-Layer Films Enable Needle-Free Therapy Using Slot-die Coating
Imagine Managing Diabetes or Obesity Without Needles
In a new research article, “Layer-by-Layer Polymeric Films: A Novel Approach to Buccal GLP-1 Delivery”, researchers from the Technical University of Denmark and Novo Nordisk investigated whether ultra-thin multilayer polymer films could deliver GLP-1 through the inner cheek, offering a non-invasive alternative to injectable drugs.
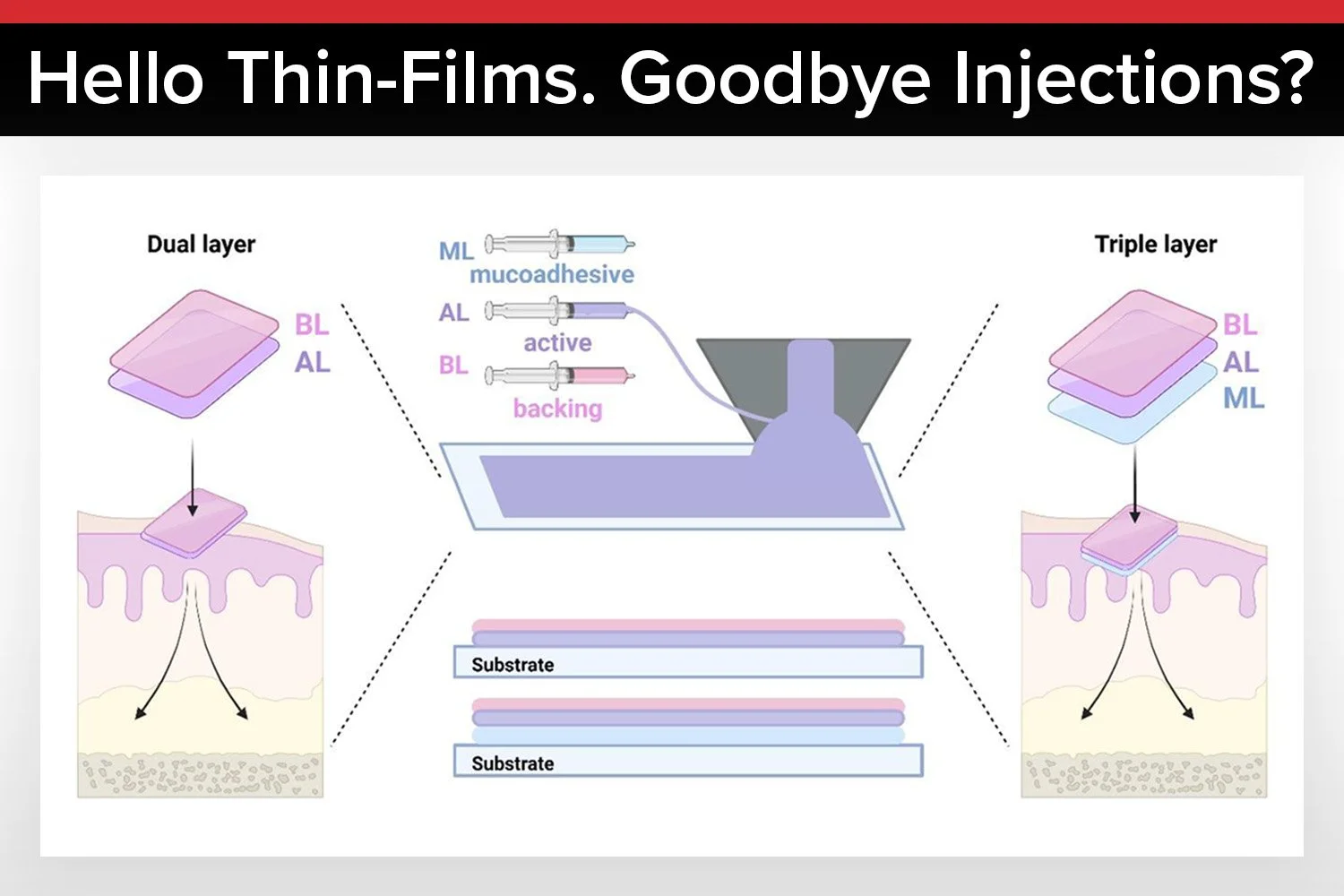
Using infinityPV’s Slot-die Coater the team created dual- and triple-layer films that release medication in a controlled way. The films attach to the cheek, allowing the drug to enter the bloodstream directly, bypassing the stomach and avoiding the need for injections. This could mean better absorption, fewer side effects, and a much easier experience for patients.
Key Highlights
The films demonstrated strong protection of peptide drugs while enabling controlled and sustained release.
The system showed promising transport across buccal tissue, supporting the potential for injection-free therapies.
Layer-by-layer assembly enabled precise control of film structure, composition, and drug loading.
The study developed multilayer polymer films for buccal delivery of GLP-1 using advanced thin-film fabrication methods using the infinityPV Slot-die Coater.
The infinityPV Slot-die Coater was used to produce uniform layers with controlled thickness, ensuring reproducible film performance.
Understanding Buccal Drug Delivery and Its Growing Importance
Delivering medication through the inner cheek may sound unconventional, yet it represents a powerful alternative to traditional delivery routes. The buccal mucosa offers a highly vascularized surface that allows drugs to enter the bloodstream directly. This pathway bypasses the digestive tract, which is known to degrade sensitive biological drugs such as peptides and proteins.
GLP-1 receptor agonists fall into this category. When taken orally, they often break down before they can provide therapeutic benefit. Injectable formats overcome this problem but introduce new challenges related to patient comfort and long-term adherence. For chronic conditions such as diabetes and obesity, treatment acceptance plays a significant role in real-world outcomes.
Buccal drug delivery attempts to bridge this gap. The challenge lies in engineering materials that can remain attached to moist tissue surfaces while releasing drugs at controlled rates. Achieving that balance requires a high level of materials control, which is where multilayer polymer film technology becomes particularly valuable.
The Technology Behind Layer-by-Layer Polymeric Films
Layer-by-layer assembly is a thin-film fabrication technique that builds coatings through sequential deposition of oppositely charged materials. Each layer contributes specific chemical or mechanical functions. By stacking these layers in a carefully designed sequence, researchers can tailor drug storage, release behavior, adhesion strength, and mechanical flexibility.
In this research, the polymeric films were engineered to encapsulate GLP-1 molecules inside a multilayer architecture. The structure protects the peptide from environmental stress while maintaining film integrity during application inside the oral cavity. The approach also allows scientists to fine-tune release kinetics by adjusting the number and composition of layers.
One aspect that makes this technology particularly relevant to modern manufacturing is its compatibility with scalable coating methods. The researchers demonstrated film deposition using precision coating techniques. During fabrication, the infinityPV Slot-die Coater was used to produce uniform layers with controlled thickness, ensuring reproducible film performance. Slot-die coating enables highly consistent wet film formation, which is critical when working with sensitive pharmaceutical formulations that require strict quality control.
The technology represents a strong example of how thin-film processing expertise is increasingly being applied to biomedical and pharmaceutical innovations.
This Matters for Healthcare and Materials Science
The significance of this work extends beyond a single therapeutic application. GLP-1 therapies are currently among the fastest growing drug categories worldwide, driven by rising rates of metabolic diseases. Improving how these drugs are delivered could have widespread impact on healthcare systems and patient quality of life.
One of the most compelling aspects of buccal film delivery is patient compliance. Removing the need for frequent injections could significantly increase treatment acceptance. Even small improvements in adherence can lead to measurable improvements in clinical outcomes for chronic diseases.
Another important factor is drug stability. Peptide therapeutics are notoriously fragile and sensitive to temperature, enzymes, and pH variations. Multilayer polymer films create a protective microenvironment that shields the drug from degradation while maintaining bioactivity.
Controlled drug release also contributes to therapeutic effectiveness. Instead of rapid dosing spikes followed by declining concentrations, structured films can deliver drugs gradually over time. This steady release profile helps maintain consistent therapeutic levels and may reduce side effects.
Discover how lab-scale slot-die coating improves pharmaceutical and medical device development through precise, uniform coatings for testing and prototyping.
Diving Into the Methods: From Polymer Design to Biological Testing
The researchers followed a systematic approach to design, fabricate, and evaluate the multilayer films. The work began with the preparation of polymer solutions carrying complementary electrical charges. These solutions were then deposited sequentially onto substrates, allowing electrostatic attraction to form stable layers.
During the fabrication stage, thin films were built by alternating polymer adsorption steps followed by drying and stabilization. The GLP-1 molecules were integrated into selected layers within the film structure. This placement allowed the researchers to optimize drug retention while maintaining release efficiency.
After fabrication, the films underwent stability testing to determine how well the polymer environment protected GLP-1 from degradation. Analytical characterization techniques were used to track peptide integrity over time under simulated physiological conditions.
The team also evaluated release kinetics to understand how the drug diffused out of the film matrix. These experiments measured release profiles under controlled environments that mimic the buccal cavity. The results showed sustained drug release, which is considered beneficial for maintaining therapeutic concentrations.
To assess biological relevance, the researchers conducted permeation studies using buccal tissue models. These experiments examined how effectively GLP-1 could pass through mucosal barriers while maintaining biological activity. The findings supported the feasibility of delivering peptide therapeutics through polymeric films applied to the oral mucosa.
Learn why modular R2R coaters are ideal for functional thin-film research.
Future Outlook and Relevance to Industrial Manufacturing
The research provides a strong proof of concept for buccal delivery of peptide therapeutics. However, its broader significance lies in the potential for scalable manufacturing and cross-industry technology transfer.
One key opportunity involves translating laboratory film fabrication into continuous roll-to-roll processes. Sequential deposition techniques used in layer-by-layer assembly are inherently compatible with modular coating systems. Industrial coating lines could potentially produce pharmaceutical films with high throughput and reproducibility.
The technology also has potential beyond GLP-1 therapies. Multilayer polymer films could be adapted for other biologic drugs, vaccines, and hormone therapies that require controlled release and protection from degradation. The ability to customize film composition allows researchers to tailor solutions for a wide range of therapeutic molecules.
Integration with advanced coating platforms may accelerate commercialization. Continuous coating, drying, and lamination technologies already used in printed electronics and advanced materials manufacturing provide a strong foundation for scaling pharmaceutical film production.
As healthcare continues to move toward patient-centric treatment models, non-invasive delivery systems are likely to gain increased attention. Thin-film drug delivery could become an important part of this transition.
Achieve pristine, contamination-free coatings with the Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater.
Conclusion
The article presents an innovative strategy for delivering peptide-based therapeutics using multilayer polymer thin films. The research demonstrates that layer-by-layer film engineering can protect sensitive GLP-1 molecules, enable sustained drug release, and facilitate absorption through buccal mucosa. The study also highlights the growing role of precision coating technologies, including the use of slot-die coating systems, in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The findings support the feasibility of non-invasive delivery for peptide drugs while showcasing the potential for scalable thin-film production. By combining materials science, biomedical engineering, and advanced coating techniques, the research illustrates how cross-disciplinary innovation can drive new therapeutic solutions and expand the application scope of roll-to-roll compatible technologies.
Authors
Eleftheria Pantazoglou
Floriane Bahuon
Amalie Kjær Andresen
Matteo Tollemeto
Zhongyang Zhang
Ioannis Tzitzigiannis
Nazanin Zanjanizadeh Ezazi
Margarida Sacramento
João F. Mano
Gavrielle R. Untracht
Peter E. Andersen
Marco van de Weert
Ragna Berthelsen
Stephen T. Buckley
Leticia Hosta-Rigau
Jette Jacobsen
Line Hagner Nielsen
Get Professional Support for Your Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.
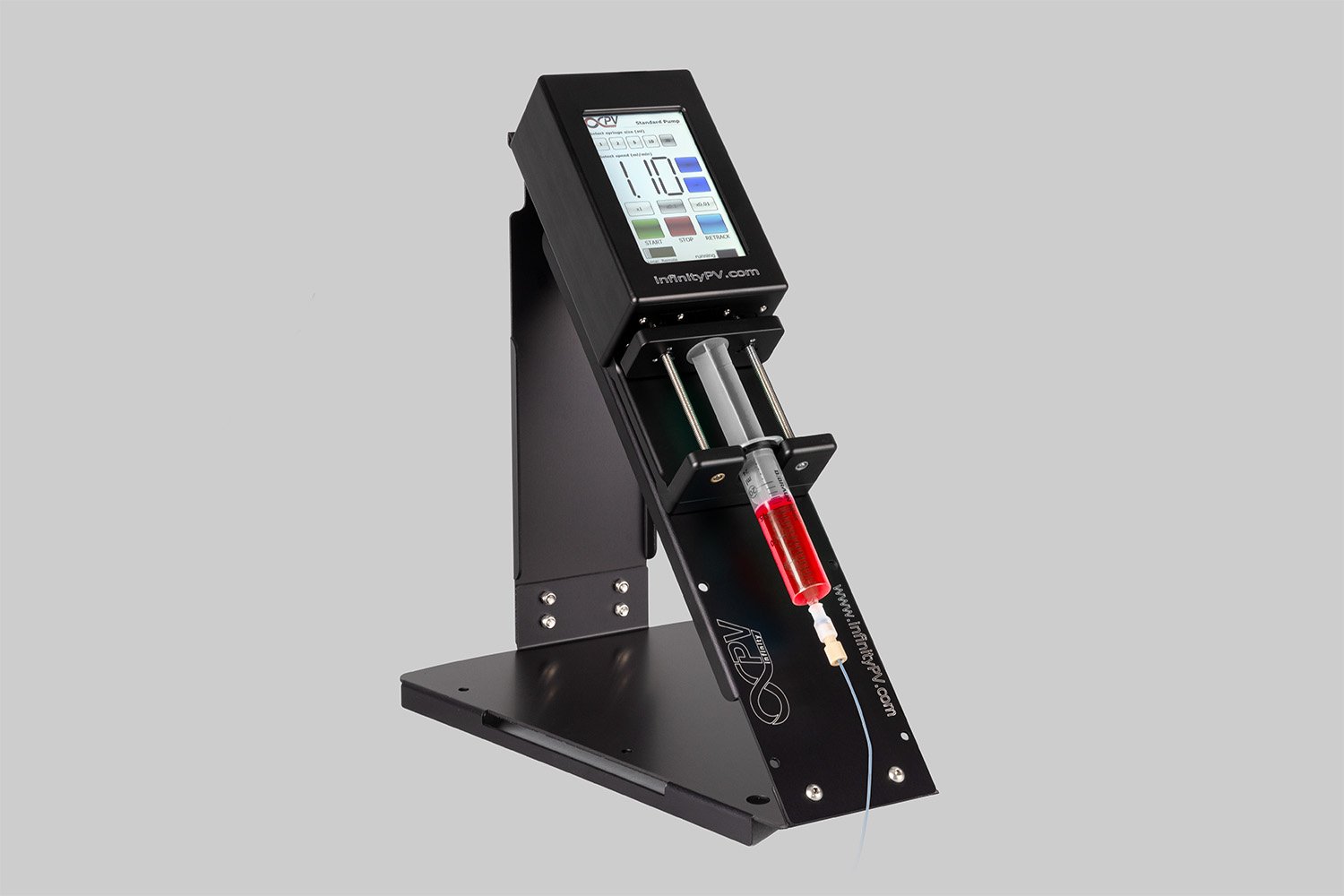
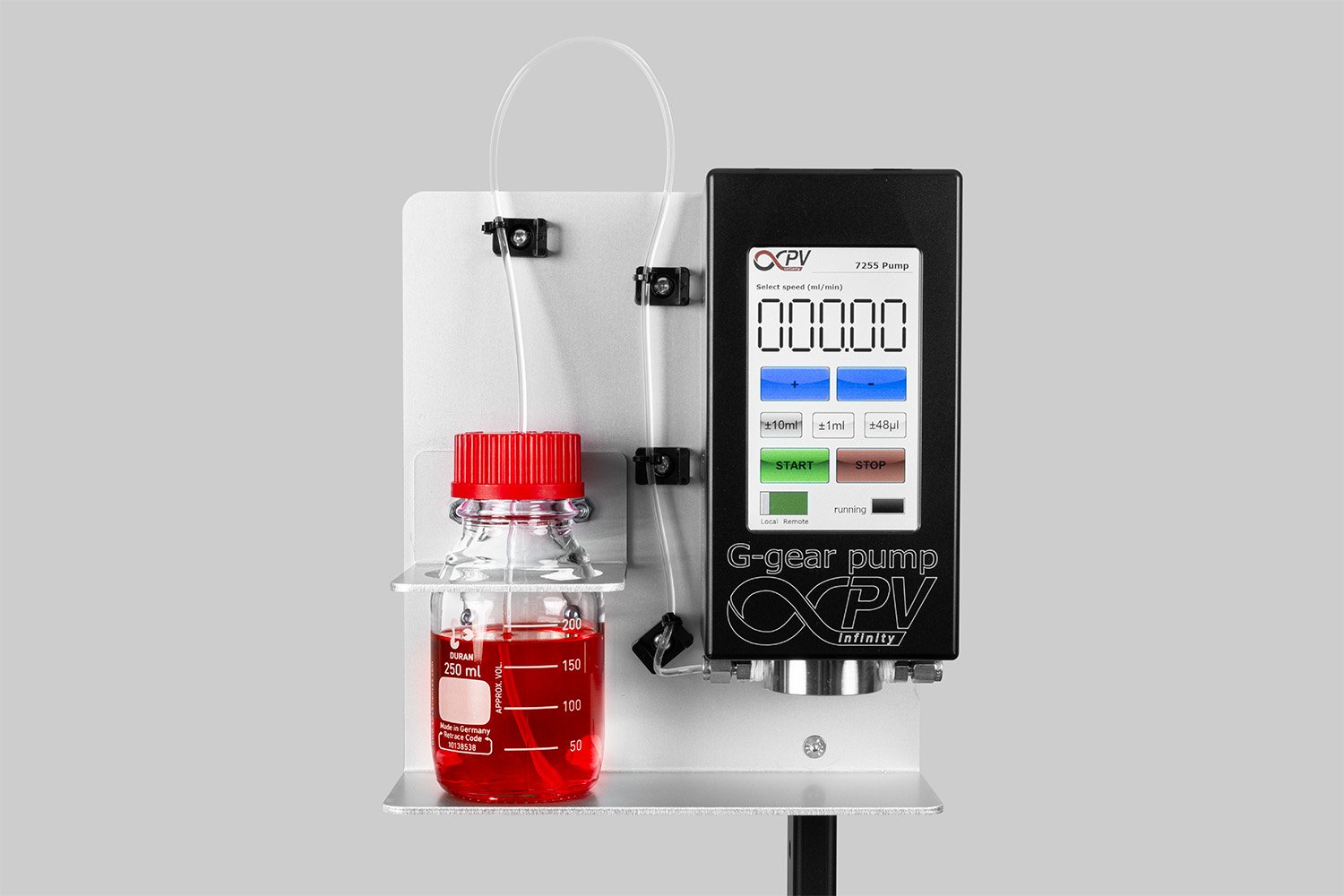
























Probably the World’s Most Compact R2R Slot-die Coater: A compact, fully integrated roll-to-roll coating platform for laboratories, complete with a mounting system, anodized rollers, a syringe pump, a 65 mm stainless slot-die head and an infrared oven system—delivering unmatched precision and scalability.